Balanced input allows optimal encoding in a stochastic binary neural network model: an analytical study
- PMID: 22359550
- PMCID: PMC3281140
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030723
Balanced input allows optimal encoding in a stochastic binary neural network model: an analytical study
Abstract
Recent neurophysiological experiments have demonstrated a remarkable effect of attention on the underlying neural activity that suggests for the first time that information encoding is indeed actively influenced by attention. Single cell recordings show that attention reduces both the neural variability and correlations in the attended condition with respect to the non-attended one. This reduction of variability and redundancy enhances the information associated with the detection and further processing of the attended stimulus. Beyond the attentional paradigm, the local activity in a neural circuit can be modulated in a number of ways, leading to the general question of understanding how the activity of such circuits is sensitive to these relatively small modulations. Here, using an analytically tractable neural network model, we demonstrate how this enhancement of information emerges when excitatory and inhibitory synaptic currents are balanced. In particular, we show that the network encoding sensitivity--as measured by the Fisher information--is maximized at the exact balance. Furthermore, we find a similar result for a more realistic spiking neural network model. As the regime of balanced inputs has been experimentally observed, these results suggest that this regime is functionally important from an information encoding standpoint.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
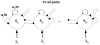
 . Current balance (top), Fano factor reduction (middle) (for a bias
. Current balance (top), Fano factor reduction (middle) (for a bias  ) and Fisher information scaled down by
) and Fisher information scaled down by  (for a bias
(for a bias  ) (bottom). (Left) Case of
) (bottom). (Left) Case of  selective populations, for which input balance occurs at
selective populations, for which input balance occurs at  (dashed line). (Right) Case of
(dashed line). (Right) Case of  selective populations, for which input balance occurs at
selective populations, for which input balance occurs at  (dashed line). All results are analytical.
(dashed line). All results are analytical.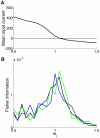
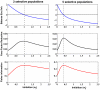
 . (A) Mean synaptic current and (B) estimated Fisher information for the population receiving an extra bias
. (A) Mean synaptic current and (B) estimated Fisher information for the population receiving an extra bias  . This quantity measures the network activity sensitivity to the bias
. This quantity measures the network activity sensitivity to the bias  and is calculated at bias
and is calculated at bias  Hz (black, blue and green curves, respectively). The Fisher information peaks around the excitatory and inhibitory synaptic currents balance. Due to noise in the data, it is almost impossible to distinguish the different curves.
Hz (black, blue and green curves, respectively). The Fisher information peaks around the excitatory and inhibitory synaptic currents balance. Due to noise in the data, it is almost impossible to distinguish the different curves.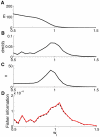
 . (A) Mean spike count
. (A) Mean spike count  , (B) its derivative with respect to the bias,
, (B) its derivative with respect to the bias,  , (C) the spike count variance
, (C) the spike count variance  and (D) the estimated Fisher information (red) and its analytical fit
and (D) the estimated Fisher information (red) and its analytical fit  (dashed black). The analytical fit works very well, showing that the Fisher information peaks around input balance because
(dashed black). The analytical fit works very well, showing that the Fisher information peaks around input balance because  also peaks there. In turn, this quantity peaks because the mean spike count
also peaks there. In turn, this quantity peaks because the mean spike count  has, with respect to
has, with respect to  , a maximum (absolute) slope around balance.
, a maximum (absolute) slope around balance.References
-
- Desimone R, Duncan J. Neural mechanisms of selective visual attention. Ann Rev Neurosci. 1995;18:193–222. - PubMed
-
- Deco G, Rolls ET. Neurodynamics of biased competition and cooperation for attention: a model with spiking neurons. J Neurophysiol. 2005;94:295–313. - PubMed
-
- Rolls ET, Deco G. Computational Neuroscience of Vision. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2002.
-
- Rolls ET, Deco G. The Noisy Brain. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

