Genome-wide identification, evolutionary expansion, and expression profile of homeodomain-leucine zipper gene family in poplar (Populus trichocarpa)
- PMID: 22359569
- PMCID: PMC3281058
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031149
Genome-wide identification, evolutionary expansion, and expression profile of homeodomain-leucine zipper gene family in poplar (Populus trichocarpa)
Abstract
Background: Homeodomain-leucine zipper (HD-ZIP) proteins are plant-specific transcriptional factors known to play crucial roles in plant development. Although sequence phylogeny analysis of Populus HD-ZIPs was carried out in a previous study, no systematic analysis incorporating genome organization, gene structure, and expression compendium has been conducted in model tree species Populus thus far.
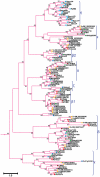
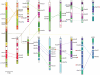
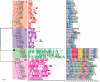
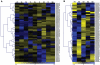
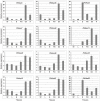
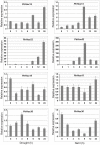
Principal findings: In this study, a comprehensive analysis of Populus HD-ZIP gene family was performed. Sixty-three full-length HD-ZIP genes were found in Populus genome. These Populus HD-ZIP genes were phylogenetically clustered into four distinct subfamilies (HD-ZIP I-IV) and predominately distributed across 17 linkage groups (LG). Fifty genes from 25 Populus paralogous pairs were located in the duplicated blocks of Populus genome and then preferentially retained during the sequential evolutionary courses. Genomic organization analyses indicated that purifying selection has played a pivotal role in the retention and maintenance of Populus HD-ZIP gene family. Microarray analysis has shown that 21 Populus paralogous pairs have been differentially expressed across different tissues and under various stresses, with five paralogous pairs showing nearly identical expression patterns, 13 paralogous pairs being partially redundant and three paralogous pairs diversifying significantly. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis performed on 16 selected Populus HD-ZIP genes in different tissues and under both drought and salinity stresses confirms their tissue-specific and stress-inducible expression patterns.
Conclusions: Genomic organizations indicated that segmental duplications contributed significantly to the expansion of Populus HD-ZIP gene family. Exon/intron organization and conserved motif composition of Populus HD-ZIPs are highly conservative in the same subfamily, suggesting the members in the same subfamilies may also have conservative functionalities. Microarray and qRT-PCR analyses showed that 89% (56 out of 63) of Populus HD-ZIPs were duplicate genes that might have been retained by substantial subfunctionalization. Taken together, these observations may lay the foundation for future functional analysis of Populus HD-ZIP genes to unravel their biological roles.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Gehring WJ, Qian YQ, Billeter M, Furukubo-Tokunaga K, Schier AF, et al. Homeodomain-DNA recognition. Cell. 1994;78:211–223. - PubMed
-
- Frank W, Phillips J, Salamini F, Bartels D. Two dehydration-inducible transcripts from the resurrection plant Craterostigma plantagineum encode interacting homeodomain-leucine zipper proteins. Plant J. 1998;15:413–421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

