Mitochondria express α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors to regulate Ca2+ accumulation and cytochrome c release: study on isolated mitochondria
- PMID: 22359587
- PMCID: PMC3281078
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031361
Mitochondria express α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors to regulate Ca2+ accumulation and cytochrome c release: study on isolated mitochondria
Abstract
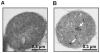
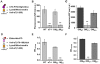
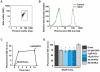
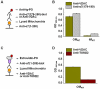
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) are ligand-gated ion channels that mediate synaptic transmission in the muscle and autonomic ganglia and regulate transmitter release in the brain. The nAChRs composed of α7 subunits are also expressed in non-excitable cells to regulate cell survival and proliferation. Up to now, functional α7 nAChRs were found exclusively on the cell plasma membrane. Here we show that they are expressed in mitochondria and regulate early pro-apoptotic events like cytochrome c release. The binding of α7-specific antibody with mouse liver mitochondria was revealed by electron microscopy. Outer membranes of mitochondria from the wild-type and β2-/- but not α7-/- mice bound α7 nAChR-specific antibody and toxins: FITC-labeled α-cobratoxin or Alexa 555-labeled α-bungarotoxin. α7 nAChR agonists (1 µM acetylcholine, 10 µM choline or 30 nM PNU-282987) impaired intramitochondrial Ca(2+) accumulation and significantly decreased cytochrome c release stimulated with either 90 µM CaCl(2) or 0.5 mM H(2)O(2). α7-specific antagonist methyllicaconitine (50 nM) did not affect Ca(2+) accumulation in mitochondria but attenuated the effects of agonists on cytochrome c release. Inhibitor of voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC) 4,4'-diisothio-cyano-2,2'-stilbene disulfonic acid (0.5 µM) decreased cytochrome c release stimulated with apoptogens similarly to α7 nAChR agonists, and VDAC was co-captured with the α7 nAChR from mitochondria outer membrane preparation in both direct and reverse sandwich ELISA. It is concluded that α7 nAChRs are expressed in mitochondria outer membrane to regulate the VDAC-mediated Ca(2+) transport and mitochondrial permeability transition.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Changeux JP. Nicotine addiction and nicotinic receptors: lessons from genetically modified mice. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010;11:389–401. - PubMed
-
- Chernyavsky AI, Arredondo J, Marubio LM, Grando SA. Differential regulation of keratinocyte chemokinesis and chemotaxis through distinct nicotinic receptor subtypes. J Cell Sci. 2004;117(Pt 23):5665–5679. - PubMed
-
- Conti-Fine BM, Navaneetham D, Lei S, Maus ADJ. Neuronal nicotinic receptors in non-neuronal cells: new mediators of tobacco toxicity? Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;393:279–294. - PubMed
-
- Bocquet N, Prado de Carvalho L, Cartaud J, Neyton J, Le Poupon C, et al. A prokaryotic proton-gated ion channel from the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor family. Nature. 2007;445:116–119. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

