Induction of sodium/iodide symporter (NIS) expression and radioiodine uptake in non-thyroid cancer cells
- PMID: 22359623
- PMCID: PMC3281006
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031729
Induction of sodium/iodide symporter (NIS) expression and radioiodine uptake in non-thyroid cancer cells
Abstract
Background: This study was designed to explore the therapeutic potential of suppressing MAP kinase and PI3K/Akt pathways and histone deacetylase (HDAC) to induce the expression of sodium/iodide symporter (NIS) and radioiodine uptake in non-thyroid cancer cells.
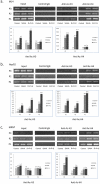
Methods: We tested the effects of the MEK inhibitor RDEA119, the Akt inhibitor perifosine, and the HDAC inhibitor SAHA on NIS expression in thirteen human cancer cell lines derived from melanoma, hepatic carcinoma, gastric carcinoma, colon carcinoma, breast carcinoma, and brain cancers. We also examined radioiodine uptake and histone acetylation at the NIS promoter in selected cells.
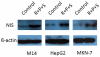
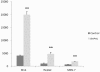
Results: Overall, the three inhibitors could induce NIS expression, to various extents, in melanoma and all the epithelial carcinoma-derived cells but not in brain cancer-derived cells. SAHA was most effective and its effect could be significantly enhanced by RDEA119 and perifosine. The expression of NIS, at both mRNA and protein levels, was most robust in the melanoma cell M14, hepatic carcinoma cell HepG2, and the gastric carcinoma cell MKN-7 cell. Radioiodine uptake was correspondingly induced, accompanied by robust increase in histone acetylation at the NIS promoter, in these cells when treated with the three inhibitors.
Conclusions: This is the first demonstration that simultaneously suppressing the MAP kinase and PI3K/Akt pathways and HDAC could induce robust NIS expression and radioiodine uptake in certain non-thyroid human cancer cells, providing novel therapeutic implications for adjunct radioiodine treatment of these cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Induction of thyroid gene expression and radioiodine uptake in thyroid cancer cells by targeting major signaling pathways.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Feb;95(2):820-8. doi: 10.1210/jc.2009-1888. Epub 2009 Dec 11. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20008023 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperation of histone deacetylase inhibitors SAHA and valproic acid in promoting sodium/iodide symporter expression and function in rat Leydig testicular carcinoma cells.Endocrine. 2014 Feb;45(1):148-52. doi: 10.1007/s12020-013-9972-4. Epub 2013 May 1. Endocrine. 2014. PMID: 23636804
-
Robust Thyroid Gene Expression and Radioiodine Uptake Induced by Simultaneous Suppression of BRAF V600E and Histone Deacetylase in Thyroid Cancer Cells.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Mar;101(3):962-71. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-3433. Epub 2016 Jan 11. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 26751190 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancement of sodium/iodide symporter expression in thyroid and breast cancer.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006 Sep;13(3):797-826. doi: 10.1677/erc.1.01143. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16954431 Review.
-
The sodium iodide symporter (NIS): regulation and approaches to targeting for cancer therapeutics.Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Sep;135(3):355-70. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2012.06.007. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Pharmacol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22750642 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular pathogenesis and mechanisms of thyroid cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2013 Mar;13(3):184-99. doi: 10.1038/nrc3431. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23429735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of 2, 3', 4, 4', 5-pentachlorobiphenyl-induced thyroid dysfunction in FRTL-5 cells.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 19;10(3):e0120133. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120133. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25789747 Free PMC article.
-
Unusual Uptake of [131I] in a Tenosynovial Giant Cell Tumour Relapse in a Patient with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer.Mol Imaging Radionucl Ther. 2022 Jun 27;31(2):145-147. doi: 10.4274/mirt.galenos.2021.40326. Mol Imaging Radionucl Ther. 2022. PMID: 35771035 Free PMC article.
-
Combined 2-deoxy glucose and metformin improves therapeutic efficacy of sodium-iodide symporter-mediated targeted radioiodine therapy in breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2015 Aug 31;7:251-65. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S84648. eCollection 2015. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2015. PMID: 26355636 Free PMC article.
-
Network analysis reveals essential proteins that regulate sodium-iodide symporter expression in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 8;10(1):21440. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78574-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33293661 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jhiang SM. Regulation of sodium/iodide symporter. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2000;1:205–15. - PubMed
-
- Spitzweg C, Morris JC. The sodium iodide symporter: its pathophysiological and therapeutic implications. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2002;57:559–74. - PubMed
-
- Baker CH, Morris JC. The sodium-iodide symporter. Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord. 2004;4:167–74. - PubMed
-
- Pacini F, Schlumberger M, Dralle H, Elisei R, Smit JW, et al. European consensus for the management of patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma of the follicular epithelium. Eur J Endocrinol. 2006;154:787–803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

