Elevated cerebral spinal fluid cytokine levels in boys with cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy correlates with MRI severity
- PMID: 22359672
- PMCID: PMC3281135
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032218
Elevated cerebral spinal fluid cytokine levels in boys with cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy correlates with MRI severity
Abstract
Background: X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) is a metabolic, peroxisomal disease that results from a mutation in the ABCD1 gene. The most severe course of ALD progression is the cerebral inflammatory and demyelinating form of the disease, cALD. To date there is very little information on the cytokine mediators in the cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) of these boys.
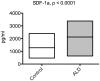
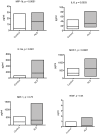
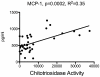
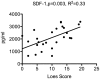
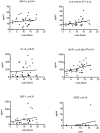
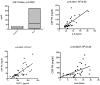
Methodology/principal findings: Measurement of 23 different cytokines was performed on CSF and serum of boys with cerebral ALD and patients without ALD. Significant elevations in CSF IL-8 (29.3±2.2 vs 12.8±1.1 pg/ml, p = 0.0001), IL-1ra (166±30 vs 8.6±6.5 pg/ml, p = 0.005), MCP-1 (610±47 vs 328±34 pg/ml, p = 0.002), and MIP-1b (14.2±1.3 vs 2.0±1.4 pg/ml, p<0.0001) were found in boys with cALD versus the control group. The only serum cytokine showing an elevation in the ALD group was SDF-1 (2124±155 vs 1175±125 pg/ml, p = 0.0001). The CSF cytokines of IL-8 and MCP-1b correlated with the Loes MRI severity score (p = 0.04 and p = 0.008 respectively), as well as the serum SDF-1 level (p = 0.002). Finally, CSF total protein was also significantly elevated in boys with cALD and correlated with both IL-8, MCP-1b (p = 0.0001 for both), as well as Loes MRI severity score (p = 0.0007).
Conclusions/significance: IL-8, IL-1ra, MCP-1, MIP-1b and CSF total protein were significantly elevated in patients with cALD; IL-8, MCP-1b, and CSF total protein levels correlated with disease severity determined by MRI. This is the largest report of CSF cytokine levels in cALD to date, and identification of these key cytokines will provide further insight into disease progression and perhaps lead to improved targeted therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Peters C. Cerebral X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: the international hematopoietic cell transplantation experience from 1982 to 1999. Blood. 2004;104:881–888. - PubMed
-
- Paintlia AS, Gilg AG, Khan M, Singh AK, Barbosa E, et al. Correlation of very long chain fatty acid accumulation and inflammatory disease progression in childhood X-ALD: implications for potential therapies. Neurobiol Dis. 2003;14:425–439. - PubMed
-
- Deon M, Wajner M, Sirtori L, Fitarelli D, Coelho D, et al. The effect of Lorenzo's oil on oxidative stress in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 2006;247:157–164. - PubMed
-
- Shapiro E, Krivit W, Lockman L, Jambaque I, Peters C, et al. Long-term effect of bone-marrow transplantation for childhood-onset cerebral X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Lancet. 2000;356:713–718. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

