MEF2 is regulated by CaMKIIδ2 and a HDAC4-HDAC5 heterodimer in vascular smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 22360269
- PMCID: PMC3632366
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20120152
MEF2 is regulated by CaMKIIδ2 and a HDAC4-HDAC5 heterodimer in vascular smooth muscle cells
Abstract
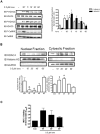
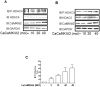
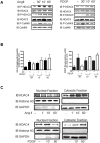
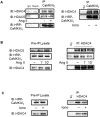
VSMCs (vascular smooth muscle cells) dedifferentiate from the contractile to the synthetic phenotype in response to acute vascular diseases such as restenosis and chronic vascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, and contribute to growth of the neointima. We demonstrated previously that balloon catheter injury of rat carotid arteries resulted in increased expression of CaMKII (Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase) IIδ(2) in the medial wall and the expanding neointima [House and Singer (2008) Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 28, 441-447]. These findings led us to hypothesize that increased expression of CaMKIIδ(2) is a positive mediator of synthetic VSMCs. HDAC (histone deacetylase) 4 and HDAC5 function as transcriptional co-repressors and are regulated in a CaMKII-dependent manner. In the present paper, we report that endogenous HDAC4 and HDAC5 in VSMCs are activated in a Ca(2+)- and CaMKIIδ(2)-dependent manner. We show further that AngII (angiotensin II)- and PDGF (platelet-derived growth factor)-dependent phosphorylation of HDAC4 and HDAC5 is reduced when CaMKIIδ(2) expression is suppressed or CaMKIIδ(2) activity is attenuated. The transcriptional activator MEF2 (myocyte-enhancer factor 2) is an important determinant of VSMC phenotype and is regulated in an HDAC-dependent manner. In the present paper, we report that stimulation of VSMCs with ionomycin or AngII potentiates MEF2's ability to bind DNA and increases the expression of established MEF2 target genes Nur77 (nuclear receptor 77) (NR4A1) and MCP1 (monocyte chemotactic protein 1) (CCL2). Suppression of CaMKIIδ(2) attenuates increased MEF2 DNA-binding activity and up-regulation of Nur77 and MCP1. Finally, we show that HDAC5 is regulated by HDAC4 in VSMCs. Suppression of HDAC4 expression and activity prevents AngII- and PDGF-dependent phosphorylation of HDAC5. Taken together, these results illustrate a mechanism by which CaMKIIδ(2) mediates MEF2-dependent gene transcription in VSMCs through regulation of HDAC4 and HDAC5.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Protein kinase A-regulated assembly of a MEF2{middle dot}HDAC4 repressor complex controls c-Jun expression in vascular smooth muscle cells.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jul 10;284(28):19027-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.000539. Epub 2009 Apr 23. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19389706 Free PMC article.
-
CaM kinase IIdeltaC phosphorylation of 14-3-3beta in vascular smooth muscle cells: activation of class II HDAC repression.Mol Cell Biochem. 2003 Jan;242(1-2):153-61. Mol Cell Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12619878
-
Angiotensin II-induced histone deacetylase 5 phosphorylation, nuclear export, and Egr-1 expression are mediated by Akt pathway in A10 vascular smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021 Apr 1;320(4):H1543-H1554. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00683.2020. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33606583
-
Exercise and MEF2-HDAC interactions.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2007 Oct;32(5):852-6. doi: 10.1139/H07-082. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2007. PMID: 18059609 Review.
-
Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II in Vascular Smooth Muscle.Adv Pharmacol. 2017;78:171-202. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2016.08.003. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Adv Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28212797 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated microRNA and mRNA network analysis of the human myometrial transcriptome in the transition from quiescence to labor.Biol Reprod. 2018 Jun 1;98(6):834-845. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioy040. Biol Reprod. 2018. PMID: 29447339 Free PMC article.
-
Co-activator binding protein PIMT mediates TNF-α induced insulin resistance in skeletal muscle via the transcriptional down-regulation of MEF2A and GLUT4.Sci Rep. 2015 Oct 15;5:15197. doi: 10.1038/srep15197. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26468734 Free PMC article.
-
CaMKII Signaling Stimulates Mef2c Activity In Vitro but Only Minimally Affects Murine Long Bone Development in vivo.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Mar 16;5:20. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2017.00020. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28361052 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin drives glucose metabolism to promote cardiac protection via OPA1-mediated HDAC5 translocation and Glut4 transcription.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Jan 29;25(1):28. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01515-8. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 39875704 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Gq Receptors and Calcineurin Activation Are Not Required for the Hypertrophic Response to Mechanical Left Ventricular Pressure Overload.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 15;9:639509. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.639509. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33659256 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Owens GK, Kumar MS, Wamhoff BR. Molecular regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation in development and disease. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:767–801. - PubMed
-
- Lindqvist A, Nilsson BO, Ekblad E, Hellstrand P. Platelet-derived growth factor receptors expressed in response to injury of differentiated vascular smooth muscle in vitro: effects on Ca2+ and growth signals. Acta Physiol Scand. 2001;173:175–184. - PubMed
-
- Gollasch M, Haase H, Ried C, Lindschau C, Morano I, Luft FC, Haller H. L-type calcium channel expression depends on the differentiated state of vascular smooth muscle cells. FASEB J. 1998;12:593–601. - PubMed
-
- Vallot O, Combettes L, Jourdon P, Inamo J, Marty I, Claret M, Lompre AM. Intracellular Ca(2+) handling in vascular smooth muscle cells is affected by proliferation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20:1225–1235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

