The neuroprotection of hydrogen sulfide against MPTP-induced dopaminergic neuron degeneration involves uncoupling protein 2 rather than ATP-sensitive potassium channels
- PMID: 22360462
- PMCID: PMC3392622
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2011.4507
The neuroprotection of hydrogen sulfide against MPTP-induced dopaminergic neuron degeneration involves uncoupling protein 2 rather than ATP-sensitive potassium channels
Abstract
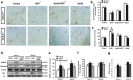
Aims: Hydrogen sulfide (H(2)S), a novel gaseous mediator, has been recognized to protect neurons from overexcitation by enhancing the activity of the adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium (K-ATP) channel. However, no direct evidence supports that the K-ATP channel contributes to the neuroprotective effect of H(2)S in neurodegeneration. Herein, wild-type and Kir6.2 knockout (Kir6.2(-/-)) mice were used to establish the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) mouse model of Parkinson's disease (PD) so as to investigate the involvement of K-ATP channels in the neuroprotection of H(2)S.
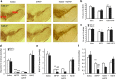
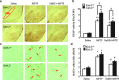
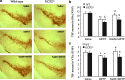
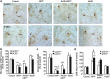
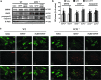
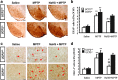
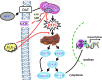
Results: Systemic administration of sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS) (an H(2)S donor, 5.6 mg/kg/day) for 7 days rescued MPTP-induced loss of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in substantia nigra compacta of both Kir6.2(+/+) and Kir6.2(-/-) mice. Consistently, NaHS (100 μM) protected primary mesencephalic neurons against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP(+))-induced cytotoxicity in both genotypes. We further found that deficiency of mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2 (UCP2), which reduces reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and functions as upstream to the K-ATP channel in determining vulnerability of DA neurons, abolished the protective effects of H(2)S against either DA neuron degeneration in the PD mouse model or MPP(+)-induced injury in primary mesencephalic neurons. Rationally, UCP2 evokes mild uncoupling, which in turn diminishes ROS accumulation in DA neurons. Furthermore, H(2)S exerted neuroprotective effect via enhancing UCP2-mediated antioxidation and subsequently suppressing ROS-triggered endoplasmic reticulum stress as well as ultimately inhibiting caspase 12-induced neuronal apoptosis.
Innovation and conclusion: H(2)S protects DA neurons against degeneration in a UCP2 rather than Kir6.2/K-ATP channel-dependent mechanism, which will give us an insight into the potential of H(2)S in terms of opening up new therapeutic avenues for PD.
Figures
References
-
- Bannenberg GL. Vieira HL. Therapeutic applications of the gaseous mediators carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulfide. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2009;19:663–682. - PubMed
-
- Deutch AY. Winder DG. A channel to neurodegeneration. Nat Med. 2006;12:17–18. - PubMed
-
- Holtz WA. O'Malley KL. Parkinsonian mimetics induce aspects of unfolded protein response in death of dopaminergic neurons. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:19367–19377. - PubMed
-
- Hong Y. Fink BD. Dillon JS. Sivitz WI. Effects of adenoviral overexpression of uncoupling protein-2 and -3 on mitochondrial respiration in insulinoma cells. Endocrinology. 2001;142:249–256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

