Nitric oxide release: part II. Therapeutic applications
- PMID: 22362384
- PMCID: PMC3341526
- DOI: 10.1039/c2cs15273h
Nitric oxide release: part II. Therapeutic applications
Abstract
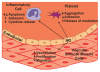
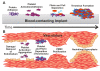
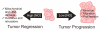
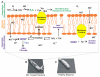
A wide range of nitric oxide (NO)-releasing materials has emerged as potential therapeutics that exploit NO's vast biological roles. Macromolecular NO-releasing scaffolds are particularly promising due to their ability to store and deliver larger NO payloads in a more controlled and effective manner compared to low molecular weight NO donors. While a variety of scaffolds (e.g., particles, dendrimers, and polymers/films) have been cleverly designed, the ultimate clinical utility of most NO-releasing macromolecules remains unrealized. Although not wholly predictive of clinical success, in vitro and in vivo investigations have enabled a preliminary evaluation of the therapeutic potential of such materials. In this tutorial review, we review the application of macromolecular NO therapies for cardiovascular disease, cancer, bacterial infections, and wound healing.
Figures

References
-
- Furchgott RF, Khan MT, Jothianandan D. Fed. Proc. 1987;46:385–385.
-
- Bauer V, Sotnikova R. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2010;29:319–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

