Survival in daily home hemodialysis and matched thrice-weekly in-center hemodialysis patients
- PMID: 22362906
- PMCID: PMC3338294
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2011080761
Survival in daily home hemodialysis and matched thrice-weekly in-center hemodialysis patients
Abstract
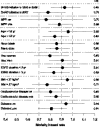
Frequent hemodialysis improves cardiovascular surrogates and quality-of-life indicators, but its effect on survival remains unclear. We used a matched-cohort design to assess relative mortality in daily home hemodialysis and thrice-weekly in-center hemodialysis patients between 2005 and 2008. We matched 1873 home hemodialysis patients with 9365 in-center patients (i.e., 1:5 ratio) selected from the prevalent population in the US Renal Data System database. Matching variables included first date of follow-up, demographic characteristics, and measures of disease severity. The cumulative incidence of death was 19.2% and 21.7% in the home hemodialysis and in-center patients, respectively. In the intention-to-treat analysis, home hemodialysis associated with a 13% lower risk for all-cause mortality than in-center hemodialysis (hazard ratio [HR], 0.87; 95% confidence interval [95% CI], 0.78-0.97). Cause-specific mortality HRs were 0.92 (95% CI, 0.78-1.09) for cardiovascular disease, 1.13 (95% CI, 0.84-1.53) for infection, 0.63 (95% CI, 0.41-0.95) for cachexia/dialysis withdrawal, 1.06 (95% CI, 0.81-1.37) for other specified cause, and 0.59 (95% CI, 0.44-0.79) for unknown cause. Findings were similar using as-treated analyses. We did not detect statistically significant evidence of heterogeneity of treatment effects in subgroup analyses. In summary, these data suggest that relative to thrice-weekly in-center hemodialysis, daily home hemodialysis associates with modest improvements in survival. Continued surveillance should strengthen inference about causes of mortality and determine whether treatment effects are homogeneous throughout the dialysis population.
Figures

Comment in
-
New observational data demonstrate that mortality is lower in patients receiving more frequent dialysis.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012 May;23(5):770-3. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2012030311. Epub 2012 Apr 12. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22499590 No abstract available.
References
-
- US Renal Data System: USRDS 2010 Annual Data Report: Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease & End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States, Bethesda, MD, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2010
-
- Block GA: Prevalence and clinical consequences of elevated Ca x P product in hemodialysis patients. Clin Nephrol 54: 318–324, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Chertow GM, Levin NW, Beck GJ, Depner TA, Eggers PW, Gassman JJ, Gorodetskaya I, Greene T, James S, Larive B, Lindsay RM, Mehta RL, Miller B, Ornt DB, Rajagopalan S, Rastogi A, Rocco MV, Schiller B, Sergeyeva O, Schulman G, Ting GO, Unruh ML, Star RA, Kliger AS, FHN Trial Group : In-center hemodialysis six times per week versus three times per week. N Engl J Med 363: 2287–2300, 2010 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Suri RS, Nesrallah GE, Mainra R, Garg AX, Lindsay RM, Greene T, Daugirdas JT: Daily hemodialysis: A systematic review. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1: 33–42, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

