Urinary tract infections caused by staphylococcus aureus DNA in comparison to the candida albicans DNA
- PMID: 22363080
- PMCID: PMC3271421
- DOI: 10.4297/najms.2011.3562
Urinary tract infections caused by staphylococcus aureus DNA in comparison to the candida albicans DNA
Abstract
Background: Bacterial DNA released upon bacterial autolysis or killed by antibiotics, hence, many inflammatogenic reactions will be established leading to serious tissue damage.
Aim: the present work aimed to elucidate the histopathological changes caused by prokaryotic (bacterial) DNA and eukaryotic (candidal) DNA.
Materials and methods: twenty one Staphylococcus aureus and 36 Candida albicans isolates were isolated from UTI patients. Viable cells and DNA of the highest antibiotic sensitive isolates were injected, intraurethraly, in mice. Results were evaluated via histopathological examination.
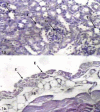
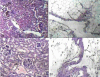
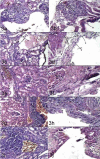
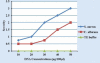
Results: Mildest reactions were obtained from mice challenged with viable C. albicans compared with those challenged with viable S. aureus. Dose-dependent histological changes were observed for both eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA. However, the eukaryotic C. albicans DNA developed less intense histological changes than S. aureus DNA.
Conclusion: microbial DNA has the ability to cause damage in murine renal system. Nevertheless, bacterial DNA caused more intense damage than candidal DNA.
Keywords: DNA; Staphylococcus aureus; UTI; candida albicans.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Candida albicans Impacts Staphylococcus aureus Alpha-Toxin Production via Extracellular Alkalinization.mSphere. 2019 Nov 13;4(6):e00780-19. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00780-19. mSphere. 2019. PMID: 31722996 Free PMC article.
-
Candida albicans Augments Staphylococcus aureus Virulence by Engaging the Staphylococcal agr Quorum Sensing System.mBio. 2019 Jun 4;10(3):e00910-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00910-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31164467 Free PMC article.
-
[Analysis of distribution and drug resistance of pathogens from the wounds of 1 310 thermal burn patients].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2018 Nov 20;34(11):802-808. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2018.11.016. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30481922 Chinese.
-
[Candida urinary tract infection with special reference to ascending pyelonephritis].Hinyokika Kiyo. 1991 Sep;37(9):969-74. Hinyokika Kiyo. 1991. PMID: 1785422 Review. Japanese.
-
Candida albicans and Staphylococcus Species: A Threatening Twosome.Front Microbiol. 2019 Sep 18;10:2162. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02162. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31620113 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bacteriology and Antibiogram of Urinary Tract Infection Among Female Patients in a Tertiary Health Facility in South Eastern Nigeria.Open Microbiol J. 2017 Oct 31;11:292-300. doi: 10.2174/1874285801711010292. eCollection 2017. Open Microbiol J. 2017. PMID: 29204224 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wagner H. Toll Meets Bacterial CpG-DNA. Immunity. 2001;14:499–502. - PubMed
-
- Stacey KJ, Young GR, Clark F, Sester DP, Roberts TL, Naik SS, et al. The Molecular Basis for the Lack of Immunostimulatory Activity of Vertebrate DNA. J Immunol. 2003;170:3614–3620. - PubMed
-
- Schindler R, Beck W, Deppisch R, Aussieker M, Wilde A, Gohl H, et al. Short Bacterial DNA Fragments: Detection in Dialysate and Induction of Cytokines. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:3207–3214. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

