Apoptosis of human cholangiocarcinoma cells induced by ESC-3 from Crocodylus siamensis bile
- PMID: 22363144
- PMCID: PMC3281230
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i7.704
Apoptosis of human cholangiocarcinoma cells induced by ESC-3 from Crocodylus siamensis bile
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the effects of ESC-3 isolated from crocodile bile on the growth and apoptosis induction of human cholangiocarcinoma cells.
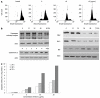
Methods: ESC-3 was isolated from crocodile bile by Sephadex LH-20 and RP-18 reversed-phase column. 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide assay was conducted to determine the effects of ESC-3 on the proliferation of human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines (QBC939, Sk-ChA-1 and MZ-ChA-1). Giemsa staining, Hoechst 33258 and acridine orange/ethidium bromide staining showed the morphological changes of Mz-ChA-1 cells exposed to ESC-3 at different concentrations. Flow cytometry with regular propidium iodide (PI) staining was performed to analyze the cell cycle distribution of Mz-ChA-1 cells and to assess apoptosis by annexin v-fluorescein isothiocyanate (V-FITC)/PI staining. Rh123 staining was used to detect the alteration of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm). The protein levels of Bax, Bcl-2, Cdk2, cytochrome c and caspase-3 were further confirmed by Western blotting.
Results: ESC-3 significantly inhibited the growth of three human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines and arrested Mz-ChA-1 cell cycle at G0/G1 phase. Mz-ChA-1 cells showed typical apoptotic morphological changes after treated with ESC-3 (10 μg/mL) for 48 h. Cell death assay indicated that Mz-ChA-1 cells underwent apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner induced by ESC-3. In addition, ESC-3 treatment could downregulate the protein level of Bcl-2 and upregulate the Bax, leading to the increase in the ratio of Bax to Bcl-2 in Mz-ChA-1 cells. Meanwhile, cytochrome c was released from the mitochondria into the cytosol, which subsequently initiated the activation of caspase-3. All these events were associated with the collapse of the mitochondrial membrane potential.
Conclusion: ESC-3, the active ingredient of crocodile bile, induced apoptosis in Mz-ChA-1 cells through the mitochondria-dependent pathway and may be a potential chemotherapeutic drug for the treatment of cholangiocarcinoma.
Keywords: Antiproliferation; Apoptosis; Cholangiocarcinoma; Crocodylus siamensis bile; Mitochondria.
Figures
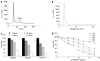


References
-
- Patel T. Increasing incidence and mortality of primary intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States. Hepatology. 2001;33:1353–1357. - PubMed
-
- Nagino M, Kamiya J, Arai T, Nishio H, Ebata T, Nimura Y. One hundred consecutive hepatobiliary resections for biliary hilar malignancy: preoperative blood donation, blood loss, transfusion, and outcome. Surgery. 2005;137:148–155. - PubMed
-
- Lazaridis KN, Gores GJ. Cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2005;128:1655–1667. - PubMed
-
- Gordaliza M. Natural products as leads to anticancer drugs. Clin and Transl Oncol. 2008;9:767–776. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

