Fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides from brown seaweeds inhibit proliferation of melanoma cells and induce apoptosis by activation of caspase-3 in vitro
- PMID: 22363242
- PMCID: PMC3280569
- DOI: 10.3390/md9122605
Fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides from brown seaweeds inhibit proliferation of melanoma cells and induce apoptosis by activation of caspase-3 in vitro
Abstract
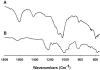
Fucose-containing sulfated polysaccharides (FCSPs) extracted from seaweeds, especially brown macro-algae, are known to possess essential bioactive properties, notably growth inhibitory effects on tumor cells. In this work, we conducted a series of in vitro studies to examine the influence of FCSPs products from Sargassumhenslowianum C. Agardh (FSAR) and Fucus vesiculosus (FVES), respectively, on proliferation of melanoma B16 cells and to investigate the underlying apoptosis promoting mechanisms. Cell viability analysis showed that both FCSPs products, i.e., FSAR and FVES, decreased the proliferation of the melanoma cells in a dose-response fashion, with FSAR being more potent at lower dosages, and FVES being relatively more anti-proliferative than FSAR at higher dosages. Flow cytometric analysis by Annexin V staining of the melanoma cells exposed to the FCSPs products confirmed that both FSAR and FVES induced apoptosis. The FCSPs-induced apoptosis was evidenced by loss of plasma membrane asymmetry and translocation of the cell membrane phospholipids and was accompanied by the activation of caspase-3. The FCSPs bioactivity is proposed to be attributable to distinct structural features of the FCSPs, particularly the presence of sulfated galactofucans (notably in S.henslowianum) and sulfated fucans (notably in F. vesiculosus). This study thus indicates that unfractionated FCSPs may exert bioactive effects on skin cancer cells via induction of apoptosis through cascades of reactions that involve activation of caspase-3.
Keywords: anti-tumor; apoptosis; bio-activity; fucoidan; fucose; sulfated polysaccharides.
Figures



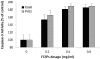

References
-
- Percival E., McDowell R. Chemistry and Enzymology of Marine Algal Polysaccharides. Academic Press; London, UK: 1967. p. 157.
-
- Patankar M.S., Oehninger S., Barnett T., Williams R.L., Clark G.F. A revised structure for fucoidan may explain some of its biological activities. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:21770–21776. - PubMed
-
- Bilan M.I., Usov A.I. Structural analysis of fucoidans. Nat. Prod. Comm. 2008;3:1639–1648.
-
- Duarte M.E., Cardoso M.A., Noseda M.D., Cerezo A.S. Structural studies on fucoidans from the brown seaweed Sargassum stenophyllum. Carbohydr. Res. 2001;333:281–293. - PubMed
-
- Tako M., Yoza E., Tohma S. Chemical characterization of acetyl fucoidan and alginate from commercially cultured Cladosiphon okamuranus. Bot. Mar. 2000;43:393–398.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

