Hypoxia-induced down-regulation of microRNA-34a promotes EMT by targeting the Notch signaling pathway in tubular epithelial cells
- PMID: 22363487
- PMCID: PMC3281867
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030771
Hypoxia-induced down-regulation of microRNA-34a promotes EMT by targeting the Notch signaling pathway in tubular epithelial cells
Abstract
Background: Hypoxia-induced renal tubular cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is an important event leading to renal fibrosis. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNA molecules that bind to their mRNA targets, thereby leading to translational repression. The role of miRNA in hypoxia-induced EMT is largely unknown.
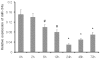
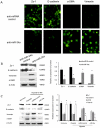
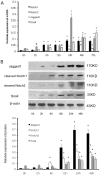
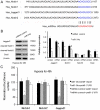
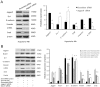
Methodology/principal findings: miRNA profiling was performed for the identification of differentially expressed miRNAs in HK-2 cells under normal and low oxygen, and the results were then verified by quantitative real time RT-PCR (qRT-PCR). The function of miRNAs in hypoxia-induced renal tubular cell EMT was assessed by the transfection of specific miRNA inhibitors and mimics. Luciferase reporter gene assays and western blot analysis were performed to validate the target genes of miR-34a. siRNA against Jagged1 was designed to investigate the role of the miR-34a-Notch pathway in hypoxia induced renal tubular cell EMT. miRNA-34a was identified as being downregulated in hypoxic renal tubular epithelial cells. Inhibition of miR-34a expression in HK-2 cells, which highly express endogenous miR-34a, promoted a mesenchymal phenotype accompanied by reduced expression of the epithelial marker Z0-1, E-cadherin and increased expression of the mesenchymal markers α-SMA and vimentin. Conversely, miR-34a mimics effectively prevented hypoxia-induced EMT. Transfection of miRNA-34a in HK-2 cells under hypoxia abolished hypoxia-induced expression of Notch1 and Jagged1 as well as Notch downstream signals, such as snail. Western blot analysis and luciferase reporter gene assays showed direct evidence for miR-34a targeting Notch1 and Jagged1. siRNAs against Jagged1 or Notch1 effectively prevented miR-34a inhibitor-induced tubular epithelial cell EMT.
Conclusions/significance: Our study provides evidence that the hypoxia-induced decrease of miR-34a expression could promote EMT in renal tubular epithelial cells by directly targeting Notch1 and Jagged1, and subsequently, Notch downstream signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI, Diederichs S. Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:228–234. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: Growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell. 2003;113:673–676. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in renal fibrogenesis: Pathologic significance, molecular mechanism, and therapeutic intervention. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:1–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

