MicroRNA 146a (miR-146a) is over-expressed during prion disease and modulates the innate immune response and the microglial activation state
- PMID: 22363497
- PMCID: PMC3281888
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030832
MicroRNA 146a (miR-146a) is over-expressed during prion disease and modulates the innate immune response and the microglial activation state
Abstract
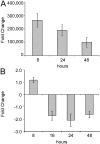
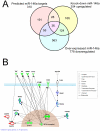
Increasing evidence supports the involvement of microRNAs (miRNAs) in inflammatory and immune processes in prion neuropathogenesis. MiRNAs are small, non-coding RNA molecules which are emerging as key regulators of numerous cellular processes. We established miR-146a over-expression in prion-infected mouse brain tissues concurrent with the onset of prion deposition and appearance of activated microglia. Expression profiling of a variety of central nervous system derived cell-lines revealed that miR-146a is preferentially expressed in cells of microglial lineage. Prominent up-regulation of miR-146a was evident in the microglial cell lines BV-2 following TLR2 or TLR4 activation and also EOC 13.31 via TLR2 that reached a maximum 24-48 hours post-stimulation, concomitant with the return to basal levels of transcription of induced cytokines. Gain- and loss-of-function studies with miR-146a revealed a substantial deregulation of inflammatory response pathways in response to TLR2 stimulation. Significant transcriptional alterations in response to miR-146a perturbation included downstream mediators of the pro-inflammatory transcription factor, nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Microarray analysis also predicts a role for miR-146a regulation of morphological changes in microglial activation states as well as phagocytic mediators of the oxidative burst such as CYBA and NOS3. Based on our results, we propose a role for miR-146a as a potent modulator of microglial function by regulating the activation state during prion induced neurodegeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-146a protects against cognitive decline induced by surgical trauma by suppressing hippocampal neuroinflammation in mice.Brain Behav Immun. 2019 May;78:188-201. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.01.020. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Brain Behav Immun. 2019. PMID: 30685530
-
microRNA-146a-5p, Neurotropic Viral Infection and Prion Disease (PrD).Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 25;22(17):9198. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179198. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-146a-5p Negatively Regulates Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Secretion and Cell Activation in Lipopolysaccharide Stimulated Human Hepatic Stellate Cells through Inhibition of Toll-Like Receptor 4 Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jul 7;17(7):1076. doi: 10.3390/ijms17071076. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27399683 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome sequencing of microglial cells stimulated with TLR3 and TLR4 ligands.BMC Genomics. 2015 Jul 10;16(1):517. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1728-5. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26159724 Free PMC article.
-
THαβ Immunological Pathway as Protective Immune Response against Prion Diseases: An Insight for Prion Infection Therapy.Viruses. 2022 Feb 17;14(2):408. doi: 10.3390/v14020408. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35216001 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Absence of miRNA-146a Differentially Alters Microglia Function and Proteome.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 5;11:1110. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01110. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32582192 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic treatment with fluoxetine using the chronic unpredictable stress model induces changes in neurotransmitters and circulating miRNAs in extracellular vesicles.Heliyon. 2023 Feb 10;9(2):e13442. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13442. eCollection 2023 Feb. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36852042 Free PMC article.
-
The mycotoxin alternariol suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in THP-1 derived macrophages targeting the NF-κB signalling pathway.Arch Toxicol. 2018 Nov;92(11):3347-3358. doi: 10.1007/s00204-018-2299-4. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Arch Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 30175388 Free PMC article.
-
Increased microRNA-146a levels in plasma of patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 2;8(9):e73272. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073272. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24023848 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression profiling of spleen microRNAs in response to two distinct type II interferons in Tetraodon nigroviridis.PLoS One. 2014 May 6;9(5):e96336. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096336. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24800866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shepard LW, Yang M, Xie P, Browning DD, Voyno-Yasenetskaya T, et al. Constitutive activation of NF-kappa B and secretion of interleukin-8 induced by the G protein-coupled receptor of kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus involve G alpha(13) and RhoA. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(49):45979–45987. - PubMed
-
- Streit WJ. Microglia as neuroprotective, immunocompetent cells of the CNS. Glia. 2002;40(2):133–139. - PubMed
-
- Liu B, Hong JS. Role of microglia in inflammation-mediated neurodegenerative diseases: Mechanisms and strategies for therapeutic intervention. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;304(1):1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

