Rice phospholipase A superfamily: organization, phylogenetic and expression analysis during abiotic stresses and development
- PMID: 22363522
- PMCID: PMC3281901
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030947
Rice phospholipase A superfamily: organization, phylogenetic and expression analysis during abiotic stresses and development
Abstract
Background: Phospholipase A (PLA) is an important group of enzymes responsible for phospholipid hydrolysis in lipid signaling. PLAs have been implicated in abiotic stress signaling and developmental events in various plants species. Genome-wide analysis of PLA superfamily has been carried out in dicot plant Arabidopsis. A comprehensive genome-wide analysis of PLAs has not been presented yet in crop plant rice.
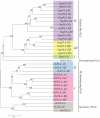
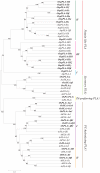
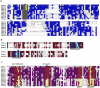
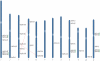
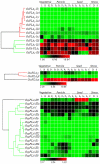
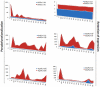
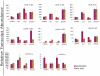
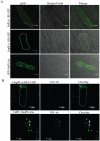
Methodology/principal findings: A comprehensive bioinformatics analysis identified a total of 31 PLA encoding genes in the rice genome, which are divided into three classes; phospholipase A(1) (PLA(1)), patatin like phospholipases (pPLA) and low molecular weight secretory phospholipase A(2) (sPLA(2)) based on their sequences and phylogeny. A subset of 10 rice PLAs exhibited chromosomal duplication, emphasizing the role of duplication in the expansion of this gene family in rice. Microarray expression profiling revealed a number of PLA members expressing differentially and significantly under abiotic stresses and reproductive development. Comparative expression analysis with Arabidopsis PLAs revealed a high degree of functional conservation between the orthologs in two plant species, which also indicated the vital role of PLAs in stress signaling and plant development across different plant species. Moreover, sub-cellular localization of a few candidates suggests their differential localization and functional role in the lipid signaling.
Conclusion/significance: The comprehensive analysis and expression profiling would provide a critical platform for the functional characterization of the candidate PLA genes in crop plants.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Munnik T, Meijer HJ. Osmotic stress activates distinct lipid and MAPK signalling pathways in plants. FEBS Lett. 2001;498:172–178. - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K. Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2006;57:781–803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

