Two novel mutations in the EYS gene are possible major causes of autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa in the Japanese population
- PMID: 22363543
- PMCID: PMC3281914
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031036
Two novel mutations in the EYS gene are possible major causes of autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa in the Japanese population
Abstract
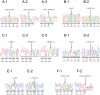
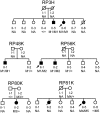
Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a highly heterogeneous genetic disease including autosomal recessive (ar), autosomal dominant (ad), and X-linked inheritance. Recently, arRP has been associated with mutations in EYS (Eyes shut homolog), which is a major causative gene for this disease. This study was conducted to determine the spectrum and frequency of EYS mutations in 100 Japanese arRP patients. To determine the prevalence of EYS mutations, all EYS exons were screened for mutations by polymerase chain reaction amplification, and sequence analysis was performed. We detected 67 sequence alterations in EYS, of which 21 were novel. Of these, 7 were very likely pathogenic mutations, 6 were possible pathogenic mutations, and 54 were predicted non-pathogenic sequence alterations. The minimum observed prevalence of distinct EYS mutations in our study was 18% (18/100, comprising 9 patients with 2 very likely pathogenic mutations and the remaining 9 with only one such mutation). Among these mutations, 2 novel truncating mutations, c.4957_4958insA (p.S1653KfsX2) and c.8868C>A (p.Y2956X), were identified in 16 patients and accounted for 57.1% (20/35 alleles) of the mutated alleles. Although these 2 truncating mutations were not detected in Japanese patients with adRP or Leber's congenital amaurosis, we detected them in Korean arRP patients. Similar to Japanese arRP results, the c.4957_4958insA mutation was more frequently detected than the c.8868C>A mutation. The 18% estimated prevalence of very likely pathogenic mutations in our study suggests a major involvement of EYS in the pathogenesis of arRP in the Japanese population. Mutation spectrum of EYS in 100 Japanese patients, including 13 distinct very likely and possible pathogenic mutations, was largely different from the previously reported spectrum in patients from non-Asian populations. Screening for c.4957_4958insA and c.8868C>A mutations in the EYS gene may therefore be very effective for the genetic testing and counseling of RP patients in Japan.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Abd El-Aziz MM, O'Driscoll CA, Kaye RS, Barragán I, El-Ashry MF, et al. Identification of novel mutations in the ortholog of Drosophila eyes shut gene (EYS) causing autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010;51:4266–4272. - PubMed
-
- Audo I, Sahel JA, Mohand-Saïd S, Lancelot ME, Antonio A, et al. EYS is a major gene for rod-cone dystrophies in France. Hum Mutat. 2010;31:E1406–1435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

