Prohibitin 1 modulates mitochondrial stress-related autophagy in human colonic epithelial cells
- PMID: 22363587
- PMCID: PMC3281932
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031231
Prohibitin 1 modulates mitochondrial stress-related autophagy in human colonic epithelial cells
Abstract
Introduction: Autophagy is an adaptive response to extracellular and intracellular stress by which cytoplasmic components and organelles, including damaged mitochondria, are degraded to promote cell survival and restore cell homeostasis. Certain genes involved in autophagy confer susceptibility to Crohn's disease. Reactive oxygen species and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), both of which are increased during active inflammatory bowel disease, promote cellular injury and autophagy via mitochondrial damage. Prohibitin (PHB), which plays a role in maintaining normal mitochondrial respiratory function, is decreased during active inflammatory bowel disease. Restoration of colonic epithelial PHB expression protects mice from experimental colitis and combats oxidative stress. In this study, we investigated the potential role of PHB in modulating mitochondrial stress-related autophagy in intestinal epithelial cells.
Methods: We measured autophagy activation in response to knockdown of PHB expression by RNA interference in Caco2-BBE and HCT116 WT and p53 null cells. The effect of exogenous PHB expression on TNFα- and IFNγ-induced autophagy was assessed. Autophagy was inhibited using Bafilomycin A(1) or siATG16L1 during PHB knockdown and the affect on intracellular oxidative stress, mitochondrial membrane potential, and cell viability were determined. The requirement of intracellular ROS in siPHB-induced autophagy was assessed using the ROS scavenger N-acetyl-L-cysteine.
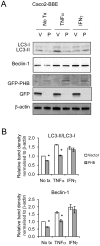
Results: TNFα and IFNγ-induced autophagy inversely correlated with PHB protein expression. Exogenous PHB expression reduced basal autophagy and TNFα-induced autophagy. Gene silencing of PHB in epithelial cells induces mitochondrial autophagy via increased intracellular ROS. Inhibition of autophagy during PHB knockdown exacerbates mitochondrial depolarization and reduces cell viability.
Conclusions: Decreased PHB levels coupled with dysfunctional autophagy renders intestinal epithelial cells susceptible to mitochondrial damage and cytotoxicity. Repletion of PHB may represent a therapeutic approach to combat oxidant and cytokine-induced mitochondrial damage in diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Beau I, Mehrpour M, Codogno P. Autophagosomes and human diseases. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011;43:460–464. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

