Prolactin secretion in healthy adults is determined by gender, age and body mass index
- PMID: 22363612
- PMCID: PMC3281966
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031305
Prolactin secretion in healthy adults is determined by gender, age and body mass index
Abstract
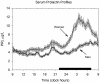
Background: Prolactin (PRL) secretion is quantifiable as mean, peak and nadir PRL concentrations, degree of irregularity (ApEn, approximate entropy) and spikiness (brief staccato-like fluctuations).
Hypothesis: Distinct PRL dynamics reflect relatively distinct (combinations of) subject variables, such as gender, age, and BMI.
Location: Clinical Research Unit.
Subjects: Seventy-four healthy adults aged 22-77 yr (41 women and 33 men), with BMI 18.3-39.4 kg/m(2).
Measures: Immunofluorometric PRL assay of 10-min samples collected for 24 hours.
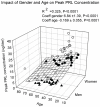
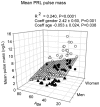
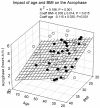
Results: Mean 24-h PRL concentration correlated jointly with gender (P<0.0001) and BMI (P = 0.01), but not with age (overall R(2) = 0.308, P<0.0001). Nadir PRL concentration correlated with gender only (P = 0.017) and peak PRL with gender (P<0.001) and negatively with age (P<0.003), overall R(2) = 0.325, P<0.0001. Forward-selection multivariate regression of PRL deconvolution results demonstrated that basal (nonpulsatile) PRL secretion tended to be associated with BMI (R(2) = 0.058, P = 0.03), pulsatile secretion with gender (R(2) = 0.152, P = 0.003), and total secretion with gender and BMI (R(2) = 0.204, P<0.0001). Pulse mass was associated with gender (P = 0.001) and with a negative tendency to age (P = 0.038). In male subjects older than 50 yr (but not in women) approximate entropy was increased (0.942±0.301 vs. 1.258±0.267, P = 0.007) compared with younger men, as well as spikiness (0.363±0.122 vs. 0463±2.12, P = 0.031). Cosinor analysis disclosed higher mesor and amplitude in females than in men, but the acrophase was gender-independent. The acrophase was determined by age and BMI (R(2) = 0.186, P = 0.001).
Conclusion: In healthy adults, selective combinations of gender, age, and BMI specify distinct PRL dynamics, thus requiring balanced representation of these variables in comparative PRL studies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Molitch ME. Prolactin. In: Melmed S, editor. The Pituitary. Cambridge MA: Blackwell Science; 1995.
-
- Kok P, Roelfsema F, Frolich M, Meinders AE, Pijl H. Prolactin release is enhanced in proportion to excess visceral fat in obese women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:4445–4449. 10.1210/jc.2003-032184 [doi];89/9/4445 [pii] - PubMed
-
- Veldhuis JD, Iranmanesh A, Wilkowski MJ, Samojlik E. Neuroendocrine alterations in the somatotropic and lactotropic axes in uremic men. Eur J Endocrinol. 1994;131:489–498. - PubMed
-
- Greenspan SL, Klibanski A, Rowe JW, Elahi D. Age alters pulsatile prolactin release: influence of dopaminergic inhibition. Am J Physiol. 1990;258:E799–E804. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

