Genome-wide SNP detection, validation, and development of an 8K SNP array for apple
- PMID: 22363718
- PMCID: PMC3283661
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031745
Genome-wide SNP detection, validation, and development of an 8K SNP array for apple
Abstract
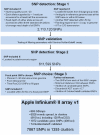
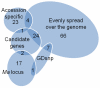
As high-throughput genetic marker screening systems are essential for a range of genetics studies and plant breeding applications, the International RosBREED SNP Consortium (IRSC) has utilized the Illumina Infinium® II system to develop a medium- to high-throughput SNP screening tool for genome-wide evaluation of allelic variation in apple (Malus×domestica) breeding germplasm. For genome-wide SNP discovery, 27 apple cultivars were chosen to represent worldwide breeding germplasm and re-sequenced at low coverage with the Illumina Genome Analyzer II. Following alignment of these sequences to the whole genome sequence of 'Golden Delicious', SNPs were identified using SoapSNP. A total of 2,113,120 SNPs were detected, corresponding to one SNP to every 288 bp of the genome. The Illumina GoldenGate® assay was then used to validate a subset of 144 SNPs with a range of characteristics, using a set of 160 apple accessions. This validation assay enabled fine-tuning of the final subset of SNPs for the Illumina Infinium® II system. The set of stringent filtering criteria developed allowed choice of a set of SNPs that not only exhibited an even distribution across the apple genome and a range of minor allele frequencies to ensure utility across germplasm, but also were located in putative exonic regions to maximize genotyping success rate. A total of 7867 apple SNPs was established for the IRSC apple 8K SNP array v1, of which 5554 were polymorphic after evaluation in segregating families and a germplasm collection. This publicly available genomics resource will provide an unprecedented resolution of SNP haplotypes, which will enable marker-locus-trait association discovery, description of the genetic architecture of quantitative traits, investigation of genetic variation (neutral and functional), and genomic selection in apple.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Peace CP, Norelli JL. Genomics approaches to crop improvement in Rosaceae. In: Folta K, Gardiner S, editors. Genetics and Genomics of Rosaceae. New York: Springer; 2009. pp. 19–53.
-
- Liebhard R, Gianfranceschi L, Koller B, Ryder CD, Tarchini R, et al. Development and characterisation of 140 new microsatellites in apple (Malus×domestica Borkh.). Molecular Breeding. 2002;10:217–241.
-
- Silfverberg-Dilworth E, Matasci CL, Van de Weg WE, Van Kaauwen MPW, Walser M, et al. Microsatellite markers spanning the apple (Malus×domestica Borkh.) genome. Tree Genetics & Genomes. 2006;2:202–224.
-
- Wang A, Aldwinckle H, Forsline P, Main D, Fazio G, et al. EST contig-based SSR linkage maps for Malus×domestica cv Royal Gala and an apple scab resistant accession of M. sieversii, the progenitor species of domestic apple. Molecular Breeding. 2011 doi: 10.1007/s11032-011-9554-1. - DOI
-
- Chagné D, Gasic K, Crowhurst RN, Han Y, Bassett HC, et al. Development of a set of SNP markers present in expressed genes of the apple. Genomics. 2008;92:353–358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

