Low-resolution molecular models reveal the oligomeric state of the PPAR and the conformational organization of its domains in solution
- PMID: 22363753
- PMCID: PMC3283691
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031852
Low-resolution molecular models reveal the oligomeric state of the PPAR and the conformational organization of its domains in solution
Abstract
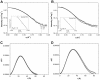
The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) regulate genes involved in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, and are targets of drugs approved for human use. Whereas the crystallographic structure of the complex of full length PPARγ and RXRα is known, structural alterations induced by heterodimer formation and DNA contacts are not well understood. Herein, we report a small-angle X-ray scattering analysis of the oligomeric state of hPPARγ alone and in the presence of retinoid X receptor (RXR). The results reveal that, in contrast with other studied nuclear receptors, which predominantly form dimers in solution, hPPARγ remains in the monomeric form by itself but forms heterodimers with hRXRα. The low-resolution models of hPPARγ/RXRα complexes predict significant changes in opening angle between heterodimerization partners (LBD) and extended and asymmetric shape of the dimer (LBD-DBD) as compared with X-ray structure of the full-length receptor bound to DNA. These differences between our SAXS models and the high-resolution crystallographic structure might suggest that there are different conformations of functional heterodimer complex in solution. Accordingly, hydrogen/deuterium exchange experiments reveal that the heterodimer binding to DNA promotes more compact and less solvent-accessible conformation of the receptor complex.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


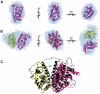




References
-
- Michalik L, Auwerx J, Berger J, Chatterjee V, Glass C, et al. International Union of Pharmacology. LXI. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2006;58:726–741. - PubMed
-
- Szanto A, Nagy L. The many faces of PPARgamma: anti-inflammatory by any means? Immunobiology. 2008;213:789–803. - PubMed
-
- Aranda A, Pascual A. Nuclear hormone receptors and gene expression. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:1269–1304. - PubMed
-
- Desvergne B, Wahli W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear control of metabolism. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:649–688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

