Prognostic variables and surgical management of foot melanoma: review of a 25-year institutional experience
- PMID: 22363851
- PMCID: PMC3262538
- DOI: 10.5402/2011/384729
Prognostic variables and surgical management of foot melanoma: review of a 25-year institutional experience
Abstract
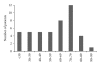
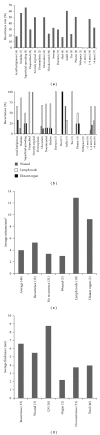
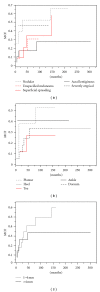
Introduction. Cutaneous foot melanoma is rare, challenging to manage, and not adequately examined in the literature. This study evaluated the prognostic variables and surgical management of foot melanoma. Materials and Methods. Foot melanoma cases managed at an academic center from 1985 to 2010 were retrospectively reviewed. Results. 46 patients were identified with a broad range of demographic characteristics. Overall recurrence was 32.6%: 19% acral lentiginous, 57% nodular, 66% superficial spreading, 30% melanoma unspecified, 50% severely atypical; 53% ulcerated, 23% nonulcerated; 29% on the dorsum of the foot, 17% heel, 60% ankle, 22% toe, 50% plantar; 0% <1 mm thick, 47% 1-4 mm, 33% >4 mm. 13 had positive nodes, 4 (31%) of whom recurred. Prognostic factors and recurrence did not correlate, and survival was 96% with a median followup of 91 months. Conclusions. Aggressive management of foot melanoma may result in excellent long-term survival even following disease recurrence.
Figures

References
-
- Rigel DS, Carucci JA. Malignant melanoma: prevention, early detection, and treatment in the 21st century. Ca-A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2000;50(4):215–236. - PubMed
-
- Booher RJ, Pack GT. Malignant melanoma of the feet and hands. Surgery. 1957;42(6):1084–1121. - PubMed
-
- Veronesi U, Cascinelli N. Narrow excision (1-cm margin): a safe procedure for thin cutaneous melanoma. Archives of Surgery. 1991;126(4):438–441. - PubMed
-
- Veronesi U, Cascinelli N, Adamus J, et al. Thin stage I primary cutaneous malignant melanoma. comparison of excision with margins of 1 or 3 cm. The New England Journal of Medicine. 1988;318(18):1159–1162. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

