Glucocorticoid receptors participate in the opiate withdrawal-induced stimulation of rats NTS noradrenergic activity and in the somatic signs of morphine withdrawal
- PMID: 22364199
- PMCID: PMC3402777
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01918.x
Glucocorticoid receptors participate in the opiate withdrawal-induced stimulation of rats NTS noradrenergic activity and in the somatic signs of morphine withdrawal
Abstract
Background and purpose: Recent evidence suggests that glucocorticoid receptor (GR) is a major molecular substrate of addictive properties of drugs of abuse. Hence, we performed a series of experiments to further characterize the role of GR signalling in opiate withdrawal-induced physical signs of dependence, enhanced noradrenaline (NA) turnover in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) phosphorylation (activation) as well as GR expression in the nucleus of the solitary tract noradrenergic cell group (NTS-A₂).
Experimental approach: The role of GR signalling was assessed by i.p. pretreatment of the selective GR antagonist, mifepristone. Rats were implanted with two morphine (or placebo) pellets. Six days later, rats were pretreated with mifepristone or vehicle 30 min before naloxone and physical signs of abstinence, NA turnover, TH activation, GR expression and the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenocortical axis activity were measured using HPLC, immunoblotting and RIA.
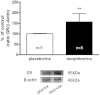
Key results: Mifepristone alleviated the somatic signs of naloxone-induced opiate withdrawal. Mifepristone attenuated the increase in the NA metabolite, 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylethylen glycol (MHPG), in the PVN, and the enhanced NA turnover observed in morphine-withdrawn rats. Mifepristone antagonized the TH phosphorylation at Ser³¹ and the expression of c-Fos expression induced by morphine withdrawal. Finally, naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal induced up-regulation of GR in the NTS.
Conclusions and implications: These results suggest that the physical signs of opiate withdrawal, TH activation and stimulation of noradrenergic pathways innervating the PVN are modulated by GR signalling. Overall, the present data suggest that drugs targeting the GR may ameliorate stress and aversive effects associated with opiate withdrawal.
© 2012 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2012 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures





Similar articles
-
CRF₂ mediates the increased noradrenergic activity in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus and the negative state of morphine withdrawal in rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Feb;162(4):851-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01090.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20973778 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid receptor but not mineralocorticoid receptor mediates the activation of ERK pathway and CREB during morphine withdrawal.Addict Biol. 2017 Mar;22(2):342-353. doi: 10.1111/adb.12328. Epub 2015 Nov 24. Addict Biol. 2017. PMID: 26598419
-
Spironolactone decreases the somatic signs of opiate withdrawal by blocking the mineralocorticoid receptors (MR).Toxicology. 2014 Dec 4;326:36-43. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2014.10.002. Epub 2014 Oct 11. Toxicology. 2014. PMID: 25308750
-
Opiate physical dependence and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors.Eur J Pharmacol. 2004 Oct 1;500(1-3):121-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.07.017. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15464026 Review.
-
Cardiac Protective Role of Heat Shock Protein 27 in the Stress Induced by Drugs of Abuse.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 21;21(10):3623. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103623. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32455528 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Early Life Stress as a Predictor of Co-Occurring Alcohol Use Disorder and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder.Alcohol Res. 2018;39(2):147-159. Alcohol Res. 2018. PMID: 31198654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AKAP150 from nucleus accumbens dopamine D1 and D2 receptor-expressing medium spiny neurons regulates morphine withdrawal.iScience. 2023 Oct 17;26(11):108227. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108227. eCollection 2023 Nov 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37953959 Free PMC article.
-
Morphine administration modulates expression of Argonaute 2 and dopamine-related transcription factors involved in midbrain dopaminergic neurons function.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Apr;168(8):1889-901. doi: 10.1111/bph.12083. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23215787 Free PMC article.
-
Astroglial Knockout of Glucocorticoid Receptor Attenuates Morphine Withdrawal Symptoms, but Not Antinociception and Tolerance in Mice.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Oct;42(7):2423-2426. doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01086-3. Epub 2021 Apr 5. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 33821329 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytes determine conditioned response to morphine via glucocorticoid receptor-dependent regulation of lactate release.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020 Jan;45(2):404-415. doi: 10.1038/s41386-019-0450-4. Epub 2019 Jun 29. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020. PMID: 31254970 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahima RS, Harlan RE. Charting of type II glucocorticoid receptor-like immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1990;39:579–604. - PubMed
-
- Ambroggi FC, Turiault M, Milet A, Deroche-Gamonet V, Parnaudeau S, Balado E, et al. Stress and addiction: glucocorticoid receptor in dopaminoceptive neurons facilitates cocaine seeking. Nat Neurosci. 2009;12:247–249. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann CG, Linthorst ACE, Holsboer F, Reul JMHM. Effect of chronic administration of selective glucocorticoid receptor antagonists on the rat hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003;28:1056–1067. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

