Propagation of tau pathology in a model of early Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 22365544
- PMCID: PMC3292759
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.11.033
Propagation of tau pathology in a model of early Alzheimer's disease
Erratum in
- Neuron. 2012 Oct 18;76(2):461
Abstract
Neurofibrillary tangles advance from layer II of the entorhinal cortex (EC-II) toward limbic and association cortices as Alzheimer's disease evolves. However, the mechanism involved in this hierarchical pattern of disease progression is unknown. We describe a transgenic mouse model in which overexpression of human tau P301L is restricted to EC-II. Tau pathology progresses from EC transgene-expressing neurons to neurons without detectable transgene expression, first to EC neighboring cells, followed by propagation to neurons downstream in the synaptic circuit such as the dentate gyrus, CA fields of the hippocampus, and cingulate cortex. Human tau protein spreads to these regions and coaggregates with endogenous mouse tau. With age, synaptic degeneration occurs in the entorhinal target zone and EC neurons are lost. These data suggest that a sequence of progressive misfolding of tau proteins, circuit-based transfer to new cell populations, and deafferentation induced degeneration are part of a process of tau-induced neurodegeneration.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
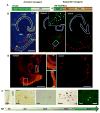
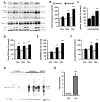
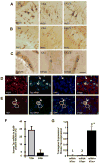
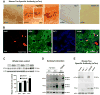
Comment in
-
In vivo spreading of tau pathology.Neuron. 2012 Feb 23;73(4):621-3. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.02.006. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 22365536
References
-
- Ballatore C, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ. Tau-mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:663–672. - PubMed
-
- Barten DM, Cadelina GW, Hoque N, DeCarr LB, Guss VL, Yang L, Sankaranarayanan S, Wes PD, Flynn ME, Meredith JE, Ahlijanian MK, Albright CF. Tau transgenic mice as models for cerebrospinal fluid tau biomarkers. J Alzheimers Dis. 2011;24:127–141. - PubMed
-
- Blennow K, Wallin A, Agren H, Spenger C, Siegfried J, Vanmechelen E. Tau protein in cerebrospinal fluid: a biochemical marker for axonal degeneration in Alzheimer disease? Mol Chem Neuropathol. 1995;26:231–245. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82:239–259. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AG026249/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21AG038835-01A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005134/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AG033670/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AG033670/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS067127/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG026249/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG08487/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K99AG33670/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 NS069811/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K08NS069811/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG038835/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG008487/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

