Pharmacologic effects of 2-methoxyestradiol on angiotensin type 1 receptor down-regulation in rat liver epithelial and aortic smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 22366193
- PMCID: PMC3322289
- DOI: 10.1016/j.genm.2012.01.008
Pharmacologic effects of 2-methoxyestradiol on angiotensin type 1 receptor down-regulation in rat liver epithelial and aortic smooth muscle cells
Abstract
Background: Delayed onset of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in female patients is not well understood, but could be due in part to the protective effect of estrogen before menopause. Experimental studies have identified the angiotensin type 1 receptor (AT1R) as a key factor in the progression of CVD.
Objective: We examined the effects of the estrogen metabolite 2-methoxyestradiol (2ME2) on AT1R expression.
Methods: Rat liver cells were exposed to 2ME2 for 24 hours, and angiotensin II (AngII) binding and AT1R mRNA expressions were assessed.
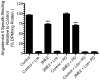
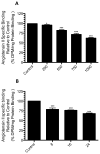
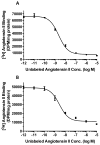
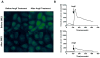
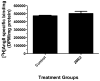
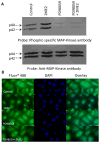
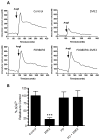
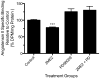
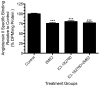
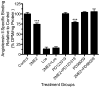
Results: In the presence of 2ME2, cells exhibited significant down-regulation of AngII binding that was both dose and time dependent, independent of estrogen receptors (ERα/ERβ). Down-regulation of AngII binding was AT1R specific, with no change in receptor affinity. Under similar conditions, we observed lower expression of AT1R mRNA, significant inhibition of AngII-mediated increase in intracellular Ca(2+), and increased phosphorylation of ERK1/2. Pretreatment of cells with the MEK inhibitor PD98059 prevented 2ME2-induced ERK1/2 phosphorylation and down-regulation of AT1R expression, which suggests that the observed inhibitory effect is mediated through ERK1/2 signaling intermediates. Similar analyses in stably transfected CHO (Chinese hamster ovary) cell lines with a constitutively active cytomegalovirus promoter showed no change in AT1R expression, which suggests that 2ME2-mediated effects are through transcriptional regulation. The effects of 2ME2 on AT1R down-regulation through ERK1/2 were consistently reproduced in primary rat aortic smooth muscle cells.
Conclusions: Because AT1R has a critical role in the control of CVD, 2ME2-induced changes in receptor expression may provide beneficial effects to the cardiovascular and other systems.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier HS Journals, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
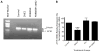
References
-
- Williams GH, Dluhy RG. Disorders of the Adrenal Cortex. 17. New York: McGraw Hill Companies Inc; 2008.
-
- Powers AC. Diabetes Mellitus. 17. New York: McGraw Hill companies Inc; 2008.
-
- Tamura K, Tanaka Y, Tsurumi Y, et al. The role of angiotensin AT1 receptor-associated protein in renin-angiotensin system regulation and function. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2007;9:121–7. - PubMed
-
- Henrion D, Kubis N, Lévy BI. Physiological and pathophysiological functions of the AT(2) subtype receptor of angiotensin II: from large arteries to the microcirculation. Hypertension. 2001;38(5):1150–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

