Arabidopsis Hexokinase-Like1 and Hexokinase1 form a critical node in mediating plant glucose and ethylene responses
- PMID: 22366209
- PMCID: PMC3320199
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.112.195636
Arabidopsis Hexokinase-Like1 and Hexokinase1 form a critical node in mediating plant glucose and ethylene responses
Abstract
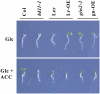
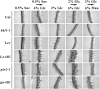
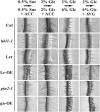
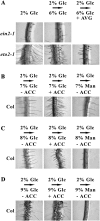
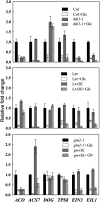
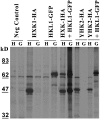
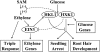
Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) Hexokinase-Like1 (HKL1) lacks glucose (Glc) phosphorylation activity and has been shown to act as a negative regulator of plant growth. Interestingly, the protein has a largely conserved Glc-binding domain, and protein overexpression was shown previously to promote seedling tolerance to exogenous 6% (w/v) Glc. Since these phenotypes occur independently of cellular Glc signaling activities, we have tested whether HKL1 might promote cross talk between the normal antagonists Glc and ethylene. We show that repression by 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) of the Glc-dependent developmental arrest of wild-type Arabidopsis seedlings requires the HKL1 protein. We also describe an unusual root hair phenotype associated with growth on high Glc medium that occurs prominently in HKL1 overexpression lines and in glucose insensitive 2-1 (gin2-1), a null mutant of Hexokinase1 (HXK1). Seedlings of these lines produce bulbous root hairs with an enlarged base after transfer from agar plates with normal medium to plates with 6% Glc. Seedling transfer to plates with 2% Glc plus ACC mimics the high-Glc effect in the HKL1 overexpression line but not in gin2-1. A similar ACC-stimulated, bulbous root hair phenotype also was observed in wild-type seedlings transferred to plates with 9% Glc. From transcript expression analyses, we found that HKL1 and HXK1 have differential roles in Glc-dependent repression of some ethylene biosynthesis genes. Since we show by coimmunoprecipitation assays that HKL1 and HXK1 can interact, these two proteins likely form a critical node in Glc signaling that mediates overlapping, but also distinct, cellular responses to Glc and ethylene treatments.
Figures
References
-
- Alonso JM, Hirayama T, Roman G, Nourizadeh S, Ecker JR. (1999) EIN2, a bifunctional transducer of ethylene and stress responses in Arabidopsis. Science 284: 2148–2152 - PubMed
-
- Argueso CT, Hansen M, Kieber JJ. (2007) Regulation of ethylene biosynthesis. J Plant Growth Regul 26: 92–105
-
- Baumberger N, Steiner M, Ryser U, Keller B, Ringli C. (2003) Synergistic interaction of the two paralogous Arabidopsis genes LRX1 and LRX2 in cell wall formation during root hair development. Plant J 35: 71–81 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

