Crystal structures of the reverse transcriptase-associated ribonuclease H domain of xenotropic murine leukemia-virus related virus
- PMID: 22366278
- PMCID: PMC3306455
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsb.2012.02.006
Crystal structures of the reverse transcriptase-associated ribonuclease H domain of xenotropic murine leukemia-virus related virus
Abstract
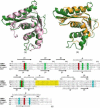
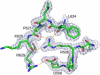
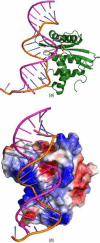
The ribonuclease H (RNase H) domain of retroviral reverse transcriptase (RT) plays a critical role in the life cycle by degrading the RNA strands of DNA/RNA hybrids. In addition, RNase H activity is required to precisely remove the RNA primers from nascent (-) and (+) strand DNA. We report here three crystal structures of the RNase H domain of xenotropic murine leukemia virus-related virus (XMRV) RT, namely (i) the previously identified construct from which helix C was deleted, (ii) the intact domain, and (iii) the intact domain complexed with an active site α-hydroxytropolone inhibitor. Enzymatic assays showed that the intact RNase H domain retained catalytic activity, whereas the variant lacking helix C was only marginally active, corroborating the importance of this helix for enzymatic activity. Modeling of the enzyme-substrate complex elucidated the essential role of helix C in binding a DNA/RNA hybrid and its likely mode of recognition. The crystal structure of the RNase H domain complexed with β-thujaplicinol clearly showed that coordination by two divalent cations mediates recognition of the inhibitor.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Adams PD, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Hung LW, Ioerger TR, McCoy AJ, et al. PHENIX: building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2002;D58:1948–1954. - PubMed
-
- Boyer PL, Gao HQ, Frank P, Clark PK, Hughes SH. The basic loop of the RNase H domain of MLV RT is important both for RNase H and for polymerase activity. Virol. 2001;282:206–213. - PubMed
-
- Brünger AT. The free R value: a novel statistical quantity for assessing the accuracy of crystal structures. Nature. 1992;355:472–474. - PubMed
-
- Cerritelli SM, Crouch RJ. Cloning, expression, and mapping of ribonucleases H of human and mouse related to bacterial RNase HI. Genomics. 1998;53:300–307. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

