Protective effect of Bacopa monniera on methyl mercury-induced oxidative stress in cerebellum of rats
- PMID: 22366895
- PMCID: PMC11498485
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-012-9813-7
Protective effect of Bacopa monniera on methyl mercury-induced oxidative stress in cerebellum of rats
Abstract
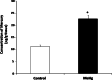
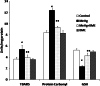
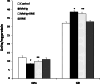
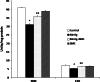
Methyl mercury (MeHg) is a ubiquitous environmental pollutant leading to neurological and developmental deficits in animals and human beings. Bacopa monniera (BM) is a perennial herb and is used as a nerve tonic in Ayurveda, a traditional medicine system in India. The objective of the present study was to investigate whether Bacopa monniera extract (BME) could potentially inhibit MeHg-induced toxicity in the cerebellum of rat brain. Male Wistar rats were administered with MeHg orally at a dose of 5 mg/kg b.w. for 21 days. Experimental rats were given MeHg and also administered with BME (40 mg/kg, orally) for 21 days. After the treatment period, we observed that MeHg exposure significantly inhibited the activities of superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase, and increased the glutathione reductase activity in cerebellum. It was also found that the level of thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances was increased with the concomitant decrease in the glutathione level in MeHg-induced rats. These alterations were prevented by the administration of BME. Behavioral interference in the MeHg-exposed animals was evident through a marked deficit in the motor performance in the rotarod task, which was completely recovered to control the levels by BME administration. The total mercury content in the cerebellum of MeHg-induced rats was also increased which was measured by atomic absorption spectrometry. The levels of NO(2) (-) and NO(3) (-) in the serum were found to be significantly increased in the MeHg-induced rats, whereas treatment with BME significantly decreased their levels in serum to near normal when compared to MeHg-induced rats. These findings strongly implicate that BM has potential to protect brain from oxidative damage resulting from MeHg-induced neurotoxicity in rat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of Bacopa monniera extract on methylmercury-induced behavioral and histopathological changes in rats.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2013 Oct;155(1):56-64. doi: 10.1007/s12011-013-9756-y. Epub 2013 Jul 20. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2013. PMID: 23872736
-
Bacopa monniera prevents from aluminium neurotoxicity in the cerebral cortex of rat brain.J Ethnopharmacol. 2007 Apr 20;111(1):56-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.10.037. Epub 2006 Nov 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17189676
-
Neuroprotective Effect of Portulaca oleraceae Ethanolic Extract Ameliorates Methylmercury Induced Cognitive Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Cerebellum and Cortex of Rat Brain.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016 Jul;172(1):155-165. doi: 10.1007/s12011-015-0546-6. Epub 2015 Nov 12. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016. PMID: 26563420
-
Oxidative stress in MeHg-induced neurotoxicity.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011 Nov 1;256(3):405-17. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2011.05.001. Epub 2011 May 9. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21601588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of methylmercury-induced neurotoxicity: evidence from experimental studies.Life Sci. 2011 Oct 10;89(15-16):555-63. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2011.05.019. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21683713 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Medicinal plants and natural products can play a significant role in mitigation of mercury toxicity.Interdiscip Toxicol. 2018 Dec;11(4):247-254. doi: 10.2478/intox-2018-0024. Epub 2019 Oct 18. Interdiscip Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 31762676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of traditional herbal plants and their polyphenols in alleviation of mercury toxicity.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):7737-7763. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03807-7. Epub 2025 Feb 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39912903 Review.
-
Effect of methylmercury on fetal neurobehavioral development: an overview of the possible mechanisms of toxicity and the neuroprotective effect of phytochemicals.Arch Toxicol. 2022 Dec;96(12):3175-3199. doi: 10.1007/s00204-022-03366-3. Epub 2022 Sep 5. Arch Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36063174 Review.
-
Antioxidant effects of Dendropanax morbifera Léveille extract in the hippocampus of mercury-exposed rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Jul 23;15:247. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0786-1. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 26201852 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of diphenyl diselenide on methylmercury toxicity in rats.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:983821. doi: 10.1155/2013/983821. Epub 2013 Dec 29. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24459674 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126 - PubMed
-
- Aschner M, Yao CP, Allen JW, Tan KH (2000) Methylmercury alters glutamate transport in astrocytes. Neurochem Int 37:199–206 - PubMed
-
- Aschner M, Syversen T, Souza DO, Rocha JB, Farina M (2007) Involvement of glutamate and reactive oxygen species in methyl mercury neurotoxicity. Braz J Med Biol Res 40:285–291 - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya SK, Kumar A, Ghosal S (1999) Effect of Bacopa monniera on animal models of Alzheimer’s disease and perturbed central cholinergic markers of cognition in rats. Res Commun Pharmacol Toxicol 4:1–12
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

