Self-assembled RNA interference microsponges for efficient siRNA delivery
- PMID: 22367004
- PMCID: PMC3965374
- DOI: 10.1038/nmat3253
Self-assembled RNA interference microsponges for efficient siRNA delivery
Abstract
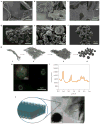
The encapsulation and delivery of short interfering RNA (siRNA) has been realized using lipid nanoparticles, cationic complexes, inorganic nanoparticles, RNA nanoparticles and dendrimers. Still, the instability of RNA and the relatively ineffectual encapsulation process of siRNA remain critical issues towards the clinical translation of RNA as a therapeutic. Here we report the synthesis of a delivery vehicle that combines carrier and cargo: RNA interference (RNAi) polymers that self-assemble into nanoscale pleated sheets of hairpin RNA, which in turn form sponge-like microspheres. The RNAi-microsponges consist entirely of cleavable RNA strands, and are processed by the cell's RNA machinery to convert the stable hairpin RNA to siRNA only after cellular uptake, thus inherently providing protection for siRNA during delivery and transport to the cytoplasm. More than half a million copies of siRNA can be delivered to a cell with the uptake of a single RNAi-microsponge. The approach could lead to novel therapeutic routes for siRNA delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




Comment in
-
siRNA delivery: Loaded-up microsponges.Nat Mater. 2012 Mar 22;11(4):268-9. doi: 10.1038/nmat3286. Nat Mater. 2012. PMID: 22437781 No abstract available.
-
siRNA as a sponge.Nat Methods. 2012 Apr;9(4):327. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1965. Nat Methods. 2012. PMID: 22563602 No abstract available.
References
-
- Semple SC, et al. Rational design of cationic lipids for siRNA delivery. Nature Biotechnol. 2010;28:172–176. - PubMed
-
- Mok H, Lee SH, Park JW, Park TG. Multimeric small interfering ribonucleic acid for highly efficient sequence-specific gene silencing. Nature Mater. 2010;9:272–278. - PubMed
-
- Liu L, et al. Self-assembled cationic peptide nanoparticles as an efficient antimicrobial agent. Nature Nanotechnol. 2009;4:457–463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

