Real-time monitoring of adherent Vero cell density and apoptosis in bioreactor processes
- PMID: 22367019
- PMCID: PMC3397106
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-011-9421-2
Real-time monitoring of adherent Vero cell density and apoptosis in bioreactor processes
Abstract
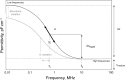
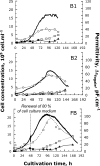
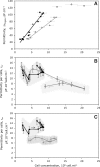
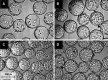
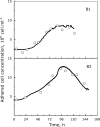
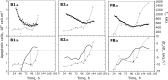
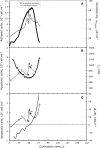
This study proposes an easy to use in situ device, based on multi-frequency permittivity measurements, to monitor the growth and death of attached Vero cells cultivated on microporous microcarriers, without any cell sampling. Vero cell densities were on-line quantified up to 10(6) cell mL(-1). Some parameters which could potentially impact Vero cell morphological and physiological states were assessed through different culture operating conditions, such as media formulation or medium feed-harvest during cell growth phase. A new method of in situ cell death detection with dielectric spectroscopy was also successfully implemented. Thus, through permittivity frequency scanning, major rises of the apoptotic cell population in bioreactor cultures were detected by monitoring the characteristic frequency of the cell population, f(c), which is one of the culture dielectric parameters. Both cell density quantification and cell apoptosis detection are strategic information in cell-based production processes as they are involved in major events of the process, such as scale-up or choice of the viral infection conditions. This new application of dielectric spectroscopy to adherent cell culture processes makes it a very promising tool for risk-mitigation strategy in industrial processes. Therefore, our results contribute to the development of Process Analytical Technology in cell-based industrial processes.
Figures
References
-
- Ansorge S, Esteban G, Schmid G. Multifrequency permittivity measurements enable on-line monitoring of changes in intracellular conductivity due to nutrient limitations during batch cultivations of CHO cells. Biotechnol Prog. 2010;26:272–283. - PubMed
-
- Ansorge S, Lanthier S, Transfiguracion J, Henry O, Kamen A (2011) Monitoring lentiviral vector production kinetics using online permittivity measurements. Biochem Eng J 54:16–25
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

