Beauvericin, a bioactive compound produced by fungi: a short review
- PMID: 22367030
- PMCID: PMC6269041
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules17032367
Beauvericin, a bioactive compound produced by fungi: a short review
Abstract
Beauvericin is a cyclic hexadepsipeptide mycotoxin, which has insecticidal, antimicrobial, antiviral and cytotoxic activities. It is a potential agent for pesticides and medicines. This paper reviews the bioactivity, fermentation and biosynthesis of the fungal product beauvericin.
Figures
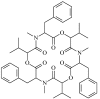

 represents the beauvericin synthetase; the dashed frame indicates the key step of beauvericin synthesis); C, The possible structure of the beauvericin synthetase (E1 is the
represents the beauvericin synthetase; the dashed frame indicates the key step of beauvericin synthesis); C, The possible structure of the beauvericin synthetase (E1 is the Similar articles
-
Beauvericin: The beauty and the beast.Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2020 Apr;75:103349. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2020.103349. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32028178 Review.
-
Calmodulin-mediated suppression of 2-ketoisovalerate reductase in Beauveria bassiana beauvericin biosynthetic pathway.Environ Microbiol. 2016 Nov;18(11):4136-4143. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13461. Epub 2016 Aug 9. Environ Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27449895
-
Cytotoxic and Antihaptotactic beauvericin analogues from precursor-directed biosynthesis with the insect pathogen Beauveria bassiana ATCC 7159.J Nat Prod. 2007 Sep;70(9):1467-71. doi: 10.1021/np070262f. Epub 2007 Sep 6. J Nat Prod. 2007. PMID: 17803266
-
The regulation of BbLaeA on the production of beauvericin and bassiatin in Beauveria bassiana.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Nov 24;38(1):1. doi: 10.1007/s11274-021-03162-8. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34817662
-
[Hyphomycetes as organisms producing cyclodepsipeptides].Antibiot Khimioter. 2010;55(3-4):35-44. Antibiot Khimioter. 2010. PMID: 20695207 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Microbial Natural Products with Antiviral Activities, Including Anti-SARS-CoV-2: A Review.Molecules. 2022 Jul 5;27(13):4305. doi: 10.3390/molecules27134305. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35807550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mycotoxin Co-Occurrence in Michigan Harvested Maize Grain.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Jun 24;14(7):431. doi: 10.3390/toxins14070431. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35878169 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Products as Mite Control Agents in Animals: A Review.Molecules. 2023 Sep 27;28(19):6818. doi: 10.3390/molecules28196818. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37836661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxicological evaluation of microbial secondary metabolites in the context of European active substance approval for plant protection products.Environ Health. 2024 Jun 4;23(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12940-024-01092-0. Environ Health. 2024. PMID: 38835048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomic Analysis Demonstrates the Impacts of Polyketide Synthases PKS14 and PKS15 on the Production of Beauvericins, Bassianolide, Enniatin A, and Ferricrocin in Entomopathogen Beauveria bassiana.Metabolites. 2023 Mar 14;13(3):425. doi: 10.3390/metabo13030425. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 36984865 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hamill R.L., Higgens G.E., Boaz H.E., Gorman M. The structure of beauvericin, a new desipeptide antibiotic toxic to Artemia salina. Tetrahedron Lett. 1969;49:4255–4258.
-
- Grove J.F., Pople M. The insecticidal activity of beauvericin and the enniatin complex. Mycopathologia. 1980;70:103–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00443075. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

