Temperature-sensitive and circadian oscillators of Neurospora crassa share components
- PMID: 22367035
- PMCID: PMC3338254
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.111.137976
Temperature-sensitive and circadian oscillators of Neurospora crassa share components
Abstract
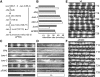
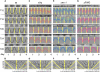
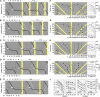
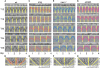
In Neurospora crassa, the interactions between products of the frequency (frq), frequency-interacting RNA helicase (frh), white collar-1 (wc-1), and white collar-2 (wc-2) genes establish a molecular circadian clockwork, called the FRQ-WC-Oscillator (FWO), which is required for the generation of molecular and overt circadian rhythmicity. In strains carrying nonfunctional frq alleles, circadian rhythms in asexual spore development (conidiation) are abolished in constant conditions, yet conidiation remains rhythmic in temperature cycles. Certain characteristics of these temperature-synchronized rhythms have been attributed to the activity of a FRQ-less oscillator (FLO). The molecular components of this FLO are as yet unknown. To test whether the FLO depends on other circadian clock components, we created a strain that carries deletions in the frq, wc-1, wc-2, and vivid (vvd) genes. Conidiation in this ΔFWO strain was still synchronized to cyclic temperature programs, but temperature-induced rhythmicity was distinct from that seen in single frq knockout strains. These results and other evidence presented indicate that components of the FWO are part of the temperature-induced FLO.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A new mutation affecting FRQ-less rhythms in the circadian system of Neurospora crassa.PLoS Genet. 2011 Jun;7(6):e1002151. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002151. Epub 2011 Jun 23. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21731506 Free PMC article.
-
Rhythmic conidiation in constant light in vivid mutants of Neurospora crassa.Genetics. 2009 Mar;181(3):917-31. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.097808. Epub 2009 Jan 12. Genetics. 2009. PMID: 19139144 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of prd circadian clock mutations on FRQ-less rhythms in Neurospora.J Biol Rhythms. 2010 Apr;25(2):71-80. doi: 10.1177/0748730409360889. J Biol Rhythms. 2010. PMID: 20348458
-
The molecular workings of the Neurospora biological clock.Novartis Found Symp. 2003;253:184-98; discussion 102-9, 198-202, 281-4. Novartis Found Symp. 2003. PMID: 14712922 Review.
-
The neurospora circadian system.J Biol Rhythms. 2004 Oct;19(5):414-24. doi: 10.1177/0748730404269116. J Biol Rhythms. 2004. PMID: 15534321 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel cryptochrome-dependent oscillator in Neurospora crassa.Genetics. 2015 Jan;199(1):233-45. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.169441. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Genetics. 2015. PMID: 25361899 Free PMC article.
-
Ribonucleoprotein complexes that control circadian clocks.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Apr 25;14(5):9018-36. doi: 10.3390/ijms14059018. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23698761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
No Evidence That Homologs of Key Circadian Clock Genes Direct Circadian Programs of Development or mRNA Abundance in Verticillium dahliae.Front Microbiol. 2020 Aug 28;11:1977. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01977. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33013740 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bruce V. G., 1960. Environmental entrainment of circadian rhythms. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 25: 29–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

