Effects of systemic ornidazole, systemic and local compound ornidazole and pefloxacin mesylate on experimental periodontitis in rats
- PMID: 22367122
- PMCID: PMC3560749
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.882514
Effects of systemic ornidazole, systemic and local compound ornidazole and pefloxacin mesylate on experimental periodontitis in rats
Abstract
Background: The purpose of the current study is to evaluate the effects of systemic ornidazole (SO) and systemic and local compound ornidazole and pefloxacin mesylate (SCOPM/LCOMP) on the inflammatory response associated with rat experimental chronic periodontitis (ECP) in sites with subgingival debridement.
Material/methods: Periodontitis was induced in male Sprague-Dawley rats by placing a thin steel ligature around the upper first molars and inoculating them with Porphyromonas gingivalis 381. After the successful induction of the rat ECP, the periodontitis rats were randomly divided into 3 different combined treatment groups: (A) SO with scaling and root planing (SRP); (B) SCOMP with SRP; and (C) LCOMP with SRP. After 2 weeks the effects of the treatments were evaluated based on gingivitis, plaque index, probing pocket depth, aspartate aminotransferase, alveolar bone loss, and hematoxylin-eosin staining of the region around the first molars.
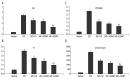
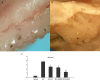
Results: After treatment, comparison with ECP was performed. The mean percentage reductions of SBI in SO, SCOPM, and LCOPM were 27.73%, 33.61%, and 58.82%, respectively. Those of PI were 33.20%, 42.80%, and 60.00%; those of PPD were 48.66%, 55.70%, and 72.48%; those of GCF-AST were 41.64%, 49.03%, and 66.42%; and those of ABL were 41.19%, 43.63%, and 54.47%, respectively. The inflammatory score of H&E showed median scores of 2.5, 1.75, 1.63, and 0.95 for ECP, SO, SCOMP, and LCOMP, respectively. All 3 treatment groups exhibited significantly reduced inflammation indicators (P<0.05). Of the 3, group C was the most effective (P<0.05).
Conclusions: Although all the combined treatment groups responded to therapy with significant resolution of the infection, adjunctive LCOMP therapy is more effective for periodontitis.
Figures

References
-
- Sanz M, Lau L, Herrera D, et al. Methods of detection of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans, Porphyromonas gingivalis and Tannerella forsythensis in periodontal microbiology, with special emphasis on advanced molecular techniques: a review. J Clin Periodontol. 2004;31(12):1034–47. - PubMed
-
- Fujii R, Saito Y, Tokura Y, et al. Characterization of bacterial flora in persistent apical periodontitis lesions. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 2009;24(6):502–5. - PubMed
-
- Haffajee AD, Socransky SS. Relationship of cigarette smoking to the subgingival microbiota. J Clin Periodontol. 2001;28(5):377–88. - PubMed
-
- von Troil B, Needleman I, Sanz M. A systematic review of the prevalence of root sensitivity following periodontal therapy. J Clin Periodontol. 2002;29(Suppl 3):173–77. discussion 195–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

