Structural characterization of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 9A capsule polysaccharide reveals role of glycosyl 6-O-acetyltransferase wcjE in serotype 9V capsule biosynthesis and immunogenicity
- PMID: 22367197
- PMCID: PMC3340191
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.346924
Structural characterization of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 9A capsule polysaccharide reveals role of glycosyl 6-O-acetyltransferase wcjE in serotype 9V capsule biosynthesis and immunogenicity
Abstract
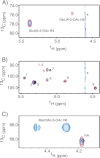
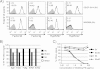
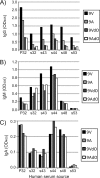
The putative capsule O-acetyltransferase gene wcjE is highly conserved across various Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes, but the role of the gene in capsule biosynthesis and bacterial fitness remains largely unclear. Isolates expressing pneumococcal serotype 9A arise from precursors expressing wcjE-associated serotype 9V through loss-of-function mutation to wcjE. To define the biosynthetic role of 9V wcjE, we characterized the structure and serological properties of serotype 9V and 9A capsule polysaccharide (PS). NMR data revealed that both 9V and 9A PS are composed of an identical pentasaccharide repeat unit, as reported previously. However, in sharp contrast to previous studies on 9A PS being devoid of any O-acetylation, we identified O-acetylation of α-glucuronic acid and α-glucose in 9A PS. In addition, 9V PS also contained -CH(2) O-acetylation of β-N-acetylmannosamine, a modification that disappeared following in vitro recombinatorial deletion of wcjE. We also show that serotyping sera and monoclonal antibodies specific for 9V and 9A bound capsule PS in an O-acetate-dependent manner. Furthermore, IgG and to a lesser extent IgM from human donors immunized with serotype 9V PS displayed stronger binding to 9V compared with 9A PS. We conclude that serotype 9V wcjE mediates 6-O-acetylation of β-N-acetylmannosamine. This PS modification can be selectively targeted by antibodies in immunized individuals, identifying a potential selective advantage for wcjE inactivation and serotype 9A emergence.
Figures



References
-
- Bentley S. D., Aanensen D. M., Mavroidi A., Saunders D., Rabbinowitsch E., Collins M., Donohoe K., Harris D., Murphy L., Quail M. A., Samuel G., Skovsted I. C., Kaltoft M. S., Barrell B., Reeves P. R., Parkhill J., Spratt B. G. (2006) Genetic analysis of the capsular biosynthetic locus from all 90 pneumococcal serotypes. PLoS Genet. 2, e31. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

