Plasma ghrelin levels are closely associated with severity and morphology of angiographically-detected coronary atherosclerosis in Chineses patients with diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 22367281
- PMCID: PMC4003365
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2011.196
Plasma ghrelin levels are closely associated with severity and morphology of angiographically-detected coronary atherosclerosis in Chineses patients with diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Aim: Low plasma ghrelin level was found to be associated with diabetes, and ghrelin was shown to inhibit pro-atherogenic changes in experimental models of atherosclerosis. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between plasma ghrelin levels and coronary atherosclerotic lesions in Chinese patients with diabetes.
Methods: Plasma ghrelin levels were measured using an ELISA kit. The severity of coronary artery disease (CAD) was determined via angiography. Composition of atherosclerotic plaques was detected via coronary CT angiography.
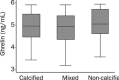
Results: A total of 178 patients with diabetes were recruited. Among the patients, 70 were diagnosed with acute coronary syndrome (ACS), 82 with stable angina pectoris (SAP) and 26 without coronary angiographic finding (controls). A negative correlation was found between ghrelin levels and the severity of the CAD, as determined via the Gensini score (r=-0.2434; P=0.0217). In diabetic patients with CAD and a complex lesion, the plasma ghrelin levels were significantly lower than in those with a simple lesion (ACS group: 3.81 ± 0.49 ng/mL vs 4.72 ± 0.50 ng/mL, P<0.0001; SAP group: 4.21 ± 0.52 ng/mL vs 4.76 ± 0.59 ng/mL, P=0.0397). Angiographically-detected complex lesion was an independent factor associated with ghrelin levels (adjusted beta coefficient=-0.67, 95% CI -0.97 to -0.37, P<0.0001).
Conclusion: Low plasma ghrelin level is closely related to angiographically-detected severity and the complex lesion morphology in Chinese diabetic patients with CAD.
Figures
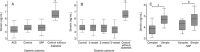

References
-
- Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature. 1999;402:656–60. - PubMed
-
- Chang L, Ren Y, Liu X, Li WG, Yang J, Geng B, et al. Protective effects of ghrelin on ischemia/reperfusion injury in the isolated rat heart. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2004;43:165–70. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu Y, Nagaya N, Teranishi Y, Imazu M, Yamamoto H, Shokawa T, et al. Ghrelin improves endothelial dysfunction through growth hormone-independent mechanisms in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;310:830–5. - PubMed
-
- Caliskan Y, Gorgulu N, Yelken B, Yazici H, Oflaz H, Elitok A, et al. Plasma ghrelin levels are associated with coronary microvascular and endothelial dysfunction in peritoneal dialysis patients. Ren Fail. 2009;31:807–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

