A distinct subset of atypical Spitz tumors is characterized by BRAF mutation and loss of BAP1 expression
- PMID: 22367297
- PMCID: PMC3354018
- DOI: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182498be5
A distinct subset of atypical Spitz tumors is characterized by BRAF mutation and loss of BAP1 expression
Abstract
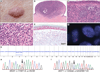
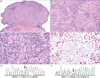
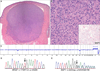
We recently reported that germline mutations in BAP1 cause a familial tumor syndrome characterized by high penetrance for melanocytic tumors with distinct clinical and histologic features. Melanocytic neoplasms in affected individuals harbored BRAF mutations, showed loss of BAP1 expression, and histologically resembled so-called "atypical Spitz tumors" (ASTs). ASTs are an ill-defined and probably heterogenous group of melanocytic tumors that display histologic features seen in both Spitz nevi and melanomas. Their biological behavior cannot be reliably predicted. In view of the histologic similarities of the familial tumors and ASTs, we hypothesized that a subset of ASTs might harbor genetic alterations seen in the familial tumors. To address this hypothesis, we analyzed 32 sporadic ASTs for BRAF mutations and for BAP1 expression. Nine (28%) sporadic ASTs showed loss of BAP1 expression, of which 8 (89%) had concomitant BRAF mutations. Only 1 of the BAP1-positive ASTs (4%) had a BRAF mutation (P<0.0001). BRAF-mutated, BAP1-negative tumors were primarily located in the dermis and were composed entirely or predominantly of epithelioid melanocytes with abundant amphophilic cytoplasm and well-defined cytoplasmic borders. Nuclei were commonly vesicular and exhibited substantial pleomorphism and conspicuous nucleoli. The combination of BRAF mutation and loss of nuclear BAP1 expression thus characterizes a subset of ASTs with distinct histologic features. The typical morphology of these tumors and BAP1 immunohistochemistry provide pathologic clues that will enable accurate identification of this subset. Future studies are necessary to determine whether this subset has a predictable clinical behavior.
Figures




References
-
- Barnhill RL. The Spitzoid lesion: rethinking Spitz tumors, atypical variants, 'Spitzoid melanoma' and risk assessment. Mod Pathol. 2006;19(Suppl 2):S21–S33. - PubMed
-
- Barnhill RL, Argenyi ZB, From L, et al. Atypical Spitz nevi/tumors: lack of consensus for diagnosis, discrimination from melanoma, and prediction of outcome. Hum Pathol. 1999;30:513–520. - PubMed
-
- Busam KJ, Murali R, Pulitzer M, et al. Atypical spitzoid melanocytic tumors with positive sentinel lymph nodes in children and teenagers, and comparison with histologically unambiguous and lethal melanomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009;33:1386–1395. - PubMed
-
- Cerroni L, Barnhill R, Elder D, et al. Melanocytic tumors of uncertain malignant potential: results of a tutorial held at the XXIX Symposium of the International Society of Dermatopathology in Graz, October 2008. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34:314–326. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

