Protease signalling: the cutting edge
- PMID: 22367392
- PMCID: PMC3321211
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2012.42
Protease signalling: the cutting edge
Abstract
Protease research has undergone a major expansion in the last decade, largely due to the extremely rapid development of new technologies, such as quantitative proteomics and in-vivo imaging, as well as an extensive use of in-vivo models. These have led to identification of physiological substrates and resulted in a paradigm shift from the concept of proteases as protein-degrading enzymes to proteases as key signalling molecules. However, we are still at the beginning of an understanding of protease signalling pathways. We have only identified a minor subset of true physiological substrates for a limited number of proteases, and their physiological regulation is still not well understood. Similarly, links with other signalling systems are not well established. Herein, we will highlight current challenges in protease research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


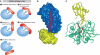

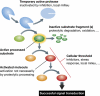
References
-
- Acehan D, Jiang X, Morgan DG, Heuser JE, Wang X, Akey CW (2002) Three-dimensional structure of the apoptosome: implications for assembly, procaspase-9 binding, and activation. Mol Cell 9: 423–432 - PubMed
-
- Al-Khunaizi M, Luke CJ, Askew YS, Pak SC, Askew DJ, Cataltepe S, Miller D, Mills DR, Tsu C, Bromme D, Irving JA, Whisstock JC, Silverman GA (2002) The serpin SQN-5 is a dual mechanistic-class inhibitor of serine and cysteine proteinases. Biochemistry 41: 3189–3199 - PubMed
-
- Alvarez VE, Kosec G, Sant’Anna C, Turk V, Cazzulo JJ, Turk B (2008) Autophagy is involved in nutritional stress response and differentiation in Trypanosoma cruzi. J Biol Chem 283: 3454–3464 - PubMed
-
- Asagiri M, Hirai T, Kunigami T, Kamano S, Gober HJ, Okamoto K, Nishikawa K, Latz E, Golenbock DT, Aoki K, Ohya K, Imai Y, Morishita Y, Miyazono K, Kato S, Saftig P, Takayanagi H (2008) Cathepsin K-dependent toll-like receptor 9 signaling revealed in experimental arthritis. Science 319: 624–627 - PubMed
-
- Bar-Shavit R, Kahn A, Wilner GD, Fenton JW II (1983) Monocyte chemotaxis: stimulation by specific exosite region in thrombin. Science 220: 728–731 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

