Genetic variant in TP63 on locus 3q28 is associated with risk of lung adenocarcinoma among never-smoking females in Asia
- PMID: 22367405
- PMCID: PMC3875137
- DOI: 10.1007/s00439-012-1144-8
Genetic variant in TP63 on locus 3q28 is associated with risk of lung adenocarcinoma among never-smoking females in Asia
Abstract
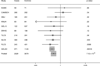
A recent genome-wide association study (GWAS) of subjects from Japan and South Korea reported a novel association between the TP63 locus on chromosome 3q28 and risk of lung adenocarcinoma (p = 7.3 × 10(-12)); however, this association did not achieve genome-wide significance (p ≤ 10(-7)) among never-smoking males or females. To determine if this association with lung cancer risk is independent of tobacco use, we genotyped the TP63 SNPs reported by the previous GWAS (rs10937405 and rs4488809) in 3,467 never-smoking female lung cancer cases and 3,787 never-smoking female controls from 10 studies conducted in Taiwan, Mainland China, South Korea, and Singapore. Genetic variation in rs10937405 was associated with risk of lung adenocarcinoma [n = 2,529 cases; p = 7.1 × 10(-8); allelic risk = 0.80, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.74-0.87]. There was also evidence of association with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung (n = 302 cases; p = 0.037; allelic risk = 0.82, 95% CI = 0.67-0.99). Our findings provide strong evidence that genetic variation in TP63 is associated with the risk of lung adenocarcinoma among Asian females in the absence of tobacco smoking.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Amos CI, Wu X, Broderick P, Gorlov IP, Gu J, Eisen T, Dong Q, Zhang Q, Gu X, Vijayakrishnan J, Sullivan K, Matakidou A, Wang Y, Mills G, Doheny K, Tsai YY, Chen WV, Shete S, Spitz MR, Houlston RS. Genome-wide association scan of tag SNPs identifies a susceptibility locus for lung cancer at 15q25.1. Nat Genet. 2008;40:616–622. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hernandez-Boussard T, Rodriguez-Tome P, Montesano R, Hainaut P. IARC p53 mutation database: a relational database to compile and analyze p53 mutations in human tumors and cell lines. International Agency for Research on Cancer. Hum Mutat. 1999;14:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Hosgood HD, III, Menashe I, Shen M, Yeager M, Yuenger J, Rajaraman P, He X, Chatterjee N, Caporaso N, Zhu Y, Chanock S, Zheng T, Lan Q. Pathway-based evaluation of 380 candidate genes and lung cancer susceptibility suggests the importance of the cell cycle pathway. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29:1938–1943. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

