Liver phospholipid transfer protein (PLTP) expression with a PLTP-null background promotes very low-density lipoprotein production in mice
- PMID: 22367708
- PMCID: PMC3409695
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.25648
Liver phospholipid transfer protein (PLTP) expression with a PLTP-null background promotes very low-density lipoprotein production in mice
Abstract
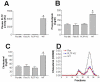
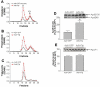
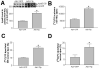
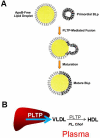
It is known that plasma phospholipid transfer protein (PLTP) activity influences lipoprotein metabolism. The liver is one of the major sites of lipoprotein production and degradation, as well as of PLTP expression. To address the impact of liver-expressed PLTP on lipoprotein metabolism, we created a mouse model that expresses PLTP in the liver acutely and specifically, with a PLTP-null background. This approach in mouse model preparations can also be used universally for evaluating the function of many other genes in the liver. We found that liver PLTP expression dramatically increases plasma levels of non-high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol (2.7-fold, P < 0.0001), non-HDL phospholipid (2.5-fold, P < 0.001), and triglyceride (51%, P < 0.01), but has no significant influence on plasma HDL lipids compared with controls. Plasma apolipoprotein (apo)B levels were also significantly increased in PLTP-expressing mice (2.2-fold, P < 0.001), but those of apoA-I were not. To explore the mechanism involved, we examined the lipidation and secretion of nascent very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), finding that liver PLTP expression significantly increases VLDL lipidation in hepatocyte microsomal lumina, and also VLDL secretion into the plasma.
Conclusion: It is possible to prepare a mouse model that expresses the gene of interest only in the liver, but not in other tissues. Our results suggest, for the first time, that the major function of liver PLTP is to drive VLDL production and makes a small contribution to plasma PLTP activity.
Copyright © 2012 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures


Comment in
-
Plasma phospholipid transfer protein: a multifaceted protein with a key role in the assembly and secretion of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins by the liver.Hepatology. 2012 Aug;56(2):415-8. doi: 10.1002/hep.25725. Epub 2012 Jul 10. Hepatology. 2012. PMID: 22430840 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Liver-specific phospholipid transfer protein deficiency reduces high-density lipoprotein and non-high-density lipoprotein production in mice.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Sep;33(9):2058-64. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301628. Epub 2013 Jul 11. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23846500 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted mutation of plasma phospholipid transfer protein gene markedly reduces high-density lipoprotein levels.J Clin Invest. 1999 Mar;103(6):907-14. doi: 10.1172/JCI5578. J Clin Invest. 1999. PMID: 10079112 Free PMC article.
-
Acute elevation of plasma PLTP activity strongly increases pre-existing atherosclerosis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008 Jul;28(7):1277-82. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.165084. Epub 2008 Apr 17. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008. PMID: 18421000
-
Phospholipid transfer protein.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2002 Apr;13(2):135-9. doi: 10.1097/00041433-200204000-00004. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2002. PMID: 11891415 Review.
-
The Role of Phospholipid Transfer Protein in the Development of Atherosclerosis.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2021 Jan 26;23(3):9. doi: 10.1007/s11883-021-00907-6. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2021. PMID: 33496859 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Specific collagen XVIII isoforms promote adipose tissue accrual via mechanisms determining adipocyte number and affect fat deposition.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jul 29;111(30):E3043-52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1405879111. Epub 2014 Jul 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25024173 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Hepatic ABCA1 deficiency is associated with delayed apolipoprotein B secretory trafficking and augmented VLDL triglyceride secretion.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017 Oct;1862(10 Pt A):1035-1043. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2017.07.001. Epub 2017 Jul 8. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017. PMID: 28694219 Free PMC article.
-
Liver X receptors and liver physiology.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021 Jun 1;1867(6):166121. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166121. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021. PMID: 33713792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phospholipid transfer protein plays a major role in the initiation of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoprotein assembly in mouse primary hepatocytes.J Biol Chem. 2015 Mar 27;290(13):8196-205. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.602748. Epub 2015 Jan 31. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25638820 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Weight Gain and Insulin Resistance in HF-Fed PLTP Deficient Mice Is Related to Altered Inflammatory Response and Plasma Transport of Gut-Derived LPS.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 30;23(21):13226. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113226. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362012 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bruce C, Beamer LJ, Tall AR. The implications of the structure of the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein on the lipid-transfer function of the cholesteryl ester transfer protein. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998;8:426–434. - PubMed
-
- Massey JB, Hickson D, She HS, Sparrow JT, Via DP, Gotto AM, Jr., Pownall HJ. Measurement and prediction of the rates of spontaneous transfer of phospholipids between plasma lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984;794:274–280. - PubMed
-
- Kawano K, Qin SC, Lin M, Tall AR, Jiang XC. Cholesteryl ester transfer protein and phospholipid transfer protein have nonoverlapping functions in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:29477–29481. - PubMed
-
- Jauhiainen M, Metso J, Pahlman R, Blomqvist S, van Tol A, Ehnholm C. Human plasma phospholipid transfer protein causes high density lipoprotein conversion. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:4032–4036. - PubMed
-
- Huuskonen J, Olkkonen VM, Ehnholm C, Metso J, Julkunen I, Jauhiainen M. Phospholipid transfer is a prerequisite for PLTP-mediated HDL conversion. Biochemistry. 2000;39:16092–16098. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
