Outcome modeling with CRLF2, IKZF1, JAK, and minimal residual disease in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Children's Oncology Group study
- PMID: 22368272
- PMCID: PMC3325039
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-11-394221
Outcome modeling with CRLF2, IKZF1, JAK, and minimal residual disease in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Children's Oncology Group study
Abstract
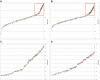
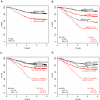
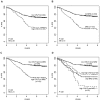
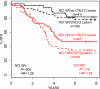
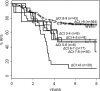
As controversy exists regarding the prognostic significance of genomic rearrangements of CRLF2 in pediatric B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) classified as standard/intermediate-risk (SR) or high-risk (HR), we assessed the prognostic significance of CRLF2 mRNA expression, CRLF2 genomic lesions (IGH@-CRLF2, P2RY8-CRLF2, CRLF2 F232C), deletion/mutation in genes frequently associated with high CRLF2 expression (IKZF1, JAK, IL7R), and minimal residual disease (MRD) in 1061 pediatric ALL patients (499 HR and 562 SR) on COG Trials P9905/P9906. Whereas very high CRLF2 expression was found in 17.5% of cases, only 51.4% of high CRLF2 expressors had CRLF2 genomic lesions. The mechanism underlying elevated CRLF2 expression in cases lacking known genomic lesions remains to be determined. All CRLF2 genomic lesions and virtually all JAK mutations were found in high CRLF2 expressors, whereas IKZF1 deletions/mutations were distributed across the full cohort. In multivariate analyses, NCI risk group, MRD, high CRLF2 expression, and IKZF1 lesions were associated with relapse-free survival. Within HR ALL, only MRD and CRLF2 expression predicted a poorer relapse-free survival; no difference was seen between cases with or without CRLF2 genomic lesions. Thus, high CRLF2 expression is associated with a very poor outcome in high-risk, but not standard-risk, ALL. This study is registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as NCT00005596 and NCT00005603.
Figures
References
-
- Russell LJ, Capasso M, Vater I, et al. Deregulated expression of cytokine receptor gene, CRLF2, is involved in lymphoid transformation in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 2009;114(13):2688–2698. - PubMed
-
- Cario G, Zimmermann M, Romey R, et al. Presence of the P2RY8-CRLF2 rearrangement is associated with a poor prognosis in non-high-risk precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children treated according to the ALL-BFM 2000 protocol. Blood. 2010;115(26):5393–5397. - PubMed
-
- Ensor HM, Schwab C, Russell LJ, et al. Demographic, clinical, and outcome features of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and CRLF2 deregulation: results from the MRC ALL97 clinical trial. Blood. 2011;117(7):2129–2136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000064/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA114762/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD044331/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA157937/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA128583/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA086011/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA98543/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA98413/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- L40 CA142226/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA098413/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA114766/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5RC2 CA14852902/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA098543/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

