Cardiac antiapoptotic and proproliferative effect of recombinant human erythropoietin in a moderate stage of chronic renal failure in the rat
- PMID: 22368404
- PMCID: PMC3283962
- DOI: 10.4103/0975-7406.92743
Cardiac antiapoptotic and proproliferative effect of recombinant human erythropoietin in a moderate stage of chronic renal failure in the rat
Abstract
Objective: Recombinant human erythropoietin (rhEPO) therapy under circumstances of moderate chronic renal failure (CRF), with yet lower kidney and heart lesion, may have a protective cardiac effect beyond the correction of anemia, whose mechanism deserves better elucidation, namely by clarifying the impact on gene expression profile of markers of apoptosis, inflammation, proliferation, angiogenesis, and lesion/stress in the heart.
Materials and methods: Four groups of rats were studied over a period of 15 weeks (n=7 each): control-without surgery and without drug treatment; rhEPO-treated with 50 IU/kg/week of rhEPO-beta; CRF-submitted to partial nephrectomy (3/4); CRF + rhEPO-CRF with rhEPO treatment after the 3rd week of surgery. The heart was collected in order to evaluate the gene expression, by real-time qPCR, of markers of apoptotic machinery, inflammation/immunology, proliferation/angiogenesis, and lesion/stress.
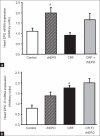
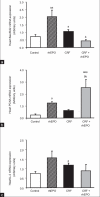
Results: The main findings obtained were (a) CRF rats have demonstrated overexpression of EPO-R in the heart without changes on EPO expression, together with overexpression of Bax/Bcl2 ratio, PCNA, and IL-2; (b) rhEPO therapy on the heart of the rats with CRF induced by partial 3/4 nephrectomy promoted nonhematopoietic protection, demonstrated by the apoptosis prevention, viewed by the Bax/Bcl2 balance, by the promotion of proliferation, due to PCNA increment, and by the immunomodulatory action, expressed by a trend to prevent the IL-2 increment.
Conclusion: In this model of moderate CRF, rhEPO treatment showed important cardiac nonhematopoietic effects, expressed mainly by the antiapoptotic and the proproliferative action, suggesting that early rhEPO therapy in moderate stages of CRF might have further therapeutic benefits.
Keywords: Apoptosis; cardiovascular protection; gene expression; moderate chronic renal failure; proliferation/angiogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recombinant human erythropoietin treatment protects the cardio-renal axis in a model of moderate chronic renal failure.Ren Fail. 2010;32(9):1073-80. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2010.509897. Ren Fail. 2010. PMID: 20863212
-
Recombinant human erythropoietin treatment of chronic renal failure patients normalizes altered phenotype and proliferation of CD4-positive T lymphocytes.Artif Organs. 2010 Mar;34(3):E77-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1594.2009.00942.x. Artif Organs. 2010. PMID: 20447038
-
Erythropoietin receptor is expressed on human peripheral blood T and B lymphocytes and monocytes and is modulated by recombinant human erythropoietin treatment.Artif Organs. 2010 Aug;34(8):654-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1594.2009.00948.x. Epub 2010 May 31. Artif Organs. 2010. PMID: 20528849
-
Therapeutic potential of erythropoietin in cardiovascular disease: erythropoiesis and beyond.Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2007 Sep;4(3):127-33. doi: 10.1007/s11897-007-0030-5. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2007. PMID: 17883987 Review.
-
The enigma of the metabolic fate of circulating erythropoietin (Epo) in view of the pharmacokinetics of the recombinant drugs rhEpo and NESP.Eur J Haematol. 2002 Nov-Dec;69(5-6):265-74. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0609.2002.02813.x. Eur J Haematol. 2002. PMID: 12460230 Review.
Cited by
-
Iron-hepcidin dysmetabolism, anemia and renal hypoxia, inflammation and fibrosis in the remnant kidney rat model.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 13;10(4):e0124048. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124048. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25867633 Free PMC article.
-
Coenzyme Q10 prevents accelerated cardiac aging in a rat model of poor maternal nutrition and accelerated postnatal growth.Mol Metab. 2013 Sep 27;2(4):480-90. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2013.09.004. eCollection 2013. Mol Metab. 2013. PMID: 24327963 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to Recombinant Human Erythropoietin Therapy in a Rat Model of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated Anemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Dec 25;17(1):28. doi: 10.3390/ijms17010028. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26712750 Free PMC article.
-
Erythropoietin facilitates the recruitment of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to sites of spinal cord injury.Exp Ther Med. 2017 May;13(5):1806-1812. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4182. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28565771 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of SDF-1/CXCR4 axis on the migration of transplanted bone mesenchymal stem cells mobilized by erythropoietin toward lesion sites following spinal cord injury.Int J Mol Med. 2015 Nov;36(5):1205-14. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2344. Epub 2015 Sep 14. Int J Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26398409 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deicher R, Hörl WH. Anaemia as a risk factor for the progression of chronic kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2003;12:139–43. - PubMed
-
- Miranda Sde P, Macedo RN, Silva Júnior GB, Daher Ede F. Cardio-renal syndrome: Pathophysiology and treatment. Rev Assoc Med Bras. 2009;55:89–94. - PubMed
-
- van der Meer P, Voors AA, Lipsic E, van Gilst WH, van Veldhuisen DJ. Erythropoietin in cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J. 2004;25:285–91. - PubMed
-
- Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Harnett JD, Kent GM, Murray DC, Barre PE. The impact of anaemia on cardiomyopathy morbidity and mortality in end-stage renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 1996;28:53–61. - PubMed
-
- Locatelli F, Conte F, Marcelli D. The impact of hematocrit levels and erythropoietin treatment on overall and cardiovascular mortality and morbidity – the experience of the Lombardy dialysis Registry. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1998;13:1642–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

