Acute effects of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on early ventricular arrhythmias after coronary occlusion in rats
- PMID: 22368415
- PMCID: PMC3284034
- DOI: 10.4103/0976-500X.92508
Acute effects of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on early ventricular arrhythmias after coronary occlusion in rats
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the acute effects of colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) on ventricular arrhythmias after coronary occlusion in rats.
Materials and methods: Male Wistar rats (10 weeks) received G-CSF (100 μg.kg(-1)) or vehicle. Thirty minutes later, animals were infarcted by coronary occlusion under artificial respiration. Electrocardiogram was monitored for 30 min to evaluate ventricular arrhythmias.
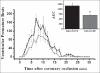
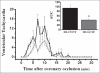
Results: G-CSF treatment reduced the number of premature ventricular beats and the number and duration of ventricular tachycardia. The incidence of ventricular fibrillation was significantly reduced by G-CSF (MI-Cont: 11.2 ± 2.4 vs. MI-GCSF: 5.4 ± 1 events; P < 0.05). However, total duration of ventricular fibrillation was not altered (MI-Cont: 84 ± 16 vs. MI-GCSF: 76 ± 13 sec).
Conclusions: Acute administration of G-CSF before coronary ligature in rats reduces the incidence of ventricular premature beats and ventricular tachycardia, suggesting a possible direct electrophysiological effect of this cytokine independently of its genomic effects. However, the data suggest that G-CSF treatment may affect the spontaneous recovery from ventricular fibrillation. Acute G-CSF administration acts directly on cardiac electrophysiology, different from chronic treatment.
Keywords: Arrhythmias; G-colony-stimulating factor; myocardial infarction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor reduces mortality by suppressing ventricular arrhythmias in acute phase of myocardial infarction in rats.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2008 Oct;52(4):375-80. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e31818a2bb0. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18841071
-
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor attenuates early ventricular expansion after experimental myocardial infarction.Cardiovasc Res. 2005 Feb 1;65(2):446-56. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.10.008. Cardiovasc Res. 2005. PMID: 15639484
-
The antiapoptotic effect of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor reduces infarct size and prevents heart failure development in rats.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011;28(1):33-40. doi: 10.1159/000331711. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21865846
-
Effectiveness and tolerability of administration of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on left ventricular function in patients with myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Clin Ther. 2007 Nov;29(11):2406-18. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.11.008. Clin Ther. 2007. PMID: 18158081 Review.
-
Pleiotropic effects of cytokines on acute myocardial infarction: G-CSF as a novel therapy for acute myocardial infarction.Curr Pharm Des. 2003;9(14):1121-7. doi: 10.2174/1381612033455008. Curr Pharm Des. 2003. PMID: 12769752 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiac Progenitor Cells in Myocardial Infarction Wound Healing: A Critical Review.Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2013 Jul;2(6):317-326. doi: 10.1089/wound.2012.0390. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2013. PMID: 24527353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implantation of a Poly-L-Lactide GCSF-Functionalized Scaffold in a Model of Chronic Myocardial Infarction.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2017 Feb;10(1):47-65. doi: 10.1007/s12265-016-9718-9. Epub 2017 Jan 23. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2017. PMID: 28116550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deindl E, Zaruba MM, Brunner S, Huber B, Mehl U, Assmann G, et al. G-CSF administration after myocardial infarction in mice attenuates late ischemic cardiomyopathy by enhanced arteriogenesis. FASEB J. 2006;20:27–36. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Takemura G, Okada H, Miyata S, Esaki M, Maruyama R, et al. Treatment with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor ameliorates chronic heart failure. Lab Invest. 2006;86:32–44. - PubMed
-
- Baldo MP, Davel AP, Damas-Souza DM, Nicoletti-Carvalho JE, Bordin S, Carvalho HF, et al. The antiapoptotic effect of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor reduces infarct size and prevents heart failure development in rats. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011;28:33–40. - PubMed
-
- Baldo MP, Davel AP, Nicoletti-Carvalho JE, Bordin S, Rossoni LV, Mill JG. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor reduces mortality by suppressing ventricular arrhythmias in acute phase of myocardial infarction in rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2008;52:375–80. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
