Visual sensor based abnormal event detection with moving shadow removal in home healthcare applications
- PMID: 22368486
- PMCID: PMC3279230
- DOI: 10.3390/s120100573
Visual sensor based abnormal event detection with moving shadow removal in home healthcare applications
Abstract
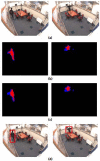
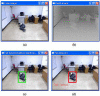
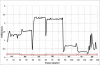
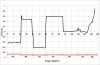
Vision-based abnormal event detection for home healthcare systems can be greatly improved using visual sensor-based techniques able to detect, track and recognize objects in the scene. However, in moving object detection and tracking processes, moving cast shadows can be misclassified as part of objects or moving objects. Shadow removal is an essential step for developing video surveillance systems. The goal of the primary is to design novel computer vision techniques that can extract objects more accurately and discriminate between abnormal and normal activities. To improve the accuracy of object detection and tracking, our proposed shadow removal algorithm is employed. Abnormal event detection based on visual sensor by using shape features variation and 3-D trajectory is presented to overcome the low fall detection rate. The experimental results showed that the success rate of detecting abnormal events was 97% with a false positive rate of 2%. Our proposed algorithm can allow distinguishing diverse fall activities such as forward falls, backward falls, and falling asides from normal activities.
Keywords: abnormal event detection; shape features variation, shadow removal algorithm; ubiquitous healthcare surveillance; visual sensor.
Figures
References
-
- Challenges of Global Aging. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Available online: http://www.aoa.gov/ (accessed on 10 September 2011).
-
- Tinetti M.E., Baker D.I., Dutcher J., Vincent J.E., Rozett R.T. Reducing the Risk of Falls among Older Adults in the Community. Peaceable Kingdom Press; Berkeley, CA, USA: 1997.
-
- Alwan M., Rajendran P.J., Kell S., Mack D., Dalal S., Wolfe M., Felde R. A smart and passive floor-vibration based fall detector for elderly. Proceedings of ICTTA '06: Information and Communication Technologies; Damascus, Syria. 24–28 April 2006; pp. 1003–1007.
-
- Purwar A., Jeong D.U., Chung W.Y. Activity monitoring from real-time triaxial accelerometer data using sensor network. Proceedings of ICCAS 2007: International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems; Seoul, Korea. 17–20 October 2007; pp. 2402–2406.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

