Right ventricular myocardium in Fallot's tetralogy: a light microscopic, morphometric and ultrastructural study
- PMID: 22368642
- PMCID: PMC3232529
Right ventricular myocardium in Fallot's tetralogy: a light microscopic, morphometric and ultrastructural study
Abstract
Aims: To analyze peroperative biopsies of RV myocardium in Tetralogy of Fallot by light microscopy, morphometry and electron microscopy in order to determine the degree of hypertrophy and degenerative changes and to correlate these changes with clinical and haemodynamic parameters.
Materials and methods: Right ventricular myocardium obtained peroperatively during surgical correction of Tetralogy of Fallot along with age-matched control samples were processed for routine light and electron microscopy using standard processing techniques. Mean cell diameter was analyzed using manual morphometric methods and ultrastructural study was carried out using a Philips transmission electron microscope.
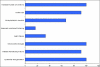
Results: The most consistent features of hypertrophy were the mitochondrial changes and increased nuclear convolutions. Majority of the patients had hypertrophy with mild to moderate degenerative changes. Severe degeneration was associated with irreversibility and was related to the severity and chronicity of the disease. There was a significant correlation of the morphological changes with clinical and haemodynamic parameters.
Conclusions: Peroperative histomorphometric and ultrastructural evaluation of the RV myocardium in Tetralogy of Fallot reflects the effect of haemodynamic stresses on the right ventricular muscle and correlates with clinical cardiac dysfunction. It may be a useful adjunct in determining the time for surgical intervention and in predicting clinical outcome.
Keywords: Heart defects; Myocardium; Tetralogy of Fallot; congenital; heart; mitochondria; ventricles.
Figures

















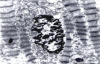













Similar articles
-
[Electron microscopical findings of the myocardium in Fallot's disease and of the ventricular septal defects (author's transl)].Zentralbl Allg Pathol. 1978;122(1-2):34-42. Zentralbl Allg Pathol. 1978. PMID: 148823 German.
-
Histopathology of the right ventricular outflow tract and its relationship to clinical outcomes and arrhythmias in patients with tetralogy of Fallot.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006 Aug;132(2):270-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2006.04.001. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006. PMID: 16872949
-
Left ventricular ultrastructure in pulmonary stenosis and in tetralogy of Fallot.Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1987;411(1):33-8. doi: 10.1007/BF00734511. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1987. PMID: 3107206
-
[Dispersion of ventricular recovery time following surgery for tetralogy of Fallot: correlation with negative prognostic factors].Cardiologia. 1998 Apr;43(4):407-15. Cardiologia. 1998. PMID: 9659799 Review. Italian.
-
[Outcome of operated Fallot's tetralogy].Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 2002 Nov;95(11):1112-8. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 2002. PMID: 12500634 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Predictors of successful pulmonary valve-sparing repair in pediatric humanitarian patients with Tetralogy of Fallot.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2025 May 28;20(1):243. doi: 10.1186/s13019-025-03475-x. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2025. PMID: 40437592 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated Growth, Differentiation, and Ploidy with Reduced Proliferation of Right Ventricular Cardiomyocytes in Children with Congenital Heart Defect Tetralogy of Fallot.Cells. 2022 Jan 5;11(1):175. doi: 10.3390/cells11010175. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35011735 Free PMC article.
-
Right Ventricular Strain in Patients With Ductal-Dependent Tetralogy of Fallot.J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2023 Jun;36(6):654-665. doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2023.03.006. Epub 2023 Mar 17. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2023. PMID: 36933850 Free PMC article.
-
Outcome of humanitarian patients with late complete repair of tetralogy of Fallot: A 13-year long single-center experience.Int J Cardiol Congenit Heart Dis. 2022 Aug 10;10:100414. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcchd.2022.100414. eCollection 2022 Dec. Int J Cardiol Congenit Heart Dis. 2022. PMID: 39713600 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jones M, Ferrans VJ. Myocardial degeneration in congenital heart disease: A comparison of morphological findings in young and old patients with congenital heart disease associated with muscular obstruction to right ventricular outflow. Am J Cardiol. 1977;39:1051. - PubMed
-
- Hibbs RG, Ferrans VJ, Black WC, Weilbaecher DG, Walsh JJ, Burch GE. Alcoholic cardiomyopathy: An electron microscopic study. Am. Heart J. 1965;766:779. - PubMed
-
- Van Noorden S, Olsen EG, Pearse AG. Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy: A histological, histochemical and ultrastructural study of biopsy material. Cardiovasc Res. 1971;5:118–131. - PubMed
-
- Nishikawa T. Ultrastructural features of the myocardium of children with dilated cardiomyopathy. Heart Vessels. 1999;14:52–56. - PubMed
-
- Sakashita I, Matsukawa J, Ando T, Asano K. Morphological comparison of infundibular pulmonary stenosis and Tetralogy of Fallot. Jpn Heart J. 1971;12:205. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
