Central venous catheters in children and neonates - what is important?
- PMID: 22368674
- PMCID: PMC3232582
Central venous catheters in children and neonates - what is important?
Abstract
Central venous access is an essential part of perioperative management for infants and children undergoing cardiac surgery for congenital heart disease. In addition, a thorough knowledge of the techniues for cannulation and placement of venous lines from the various percutaneously accessible sites is an important aspect of cardiac catheterization in this patient population. In the first of a series of papers describing the various approaches to venous access, we describe percutaneous cannulation of the subclavian vein. The standard approach, as well as potential difficulties, and how to overcome them, are described, as also the complications associated with this approach.
Keywords: Catheterization, Central Venous/adverse effects/*methods; Subclavian Vein; Venous Thrombosis/*prevention & control.
Figures








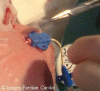
References
-
- Jonge RC, Polderman KH, Gemke RJ. Central venous catheter use in the pediatric patient: mechanical and infectious complications. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2005;6:329–39. - PubMed
-
- Karapinar B, Cura A. Complications of central venous catheterization in critically ill children. Pediatr Int. 2007;49:593–9. - PubMed
-
- Casado-Flores J, Barja J, Martino R, Serrano A, Valdivielso A. Complications of central venous catheterization in critically ill children. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2001;2:57–62. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Teresa MA, Casado-Flores J, Delgado Dominguez MA, Roqueta-Mas J, Cambra-Lasaosa F, Concha-Torre A, Fernando-Perez C. Infectious complications of percutaneous central venous catheterization in pediatric patients- A Spanish multicenter study. Intensive Care Med. 2007;33:466–76. - PubMed
-
- Breschan C, Jost R, Platzer M, Likar R. Nitinol mandril guide wire facilitates percutaneous subclavian vein cannulation in a very small preterm infant. Pediatric Anesthesia. 2006;16:366–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
