Minimally invasive removal of a giant extradural lumbar foraminal schwannoma
- PMID: 22368787
- PMCID: PMC3267373
- DOI: 10.4103/2152-7806.91141
Minimally invasive removal of a giant extradural lumbar foraminal schwannoma
Abstract
Background: Purely extradural lumbar schwannomas are rare lesions. Resection traditionally requires an open laminectomy and ipsilateral complete facectomy. Recent reports have demonstrated safety and efficacy of removal of these tumors using mini-open access devices with expandable retractors. We report a case of a giant L3 schwannoma successfully resected through a minimally invasive approach using the non-expandable Spotlight tubular retrator (Depuy Spine).
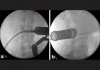
Case description: A 77-year-old woman presented with a history of chronic right leg pain, paresthesias and proximal right leg weakness. Magnetic Resonance imaging (MRI) scan revealed a large dumbbell-shaped extradural foraminal lesion at the L3-L4 level with significant extraforaminal extension. The patient underwent a minimally invasive gross total resection (GTR) of the tumor using an 18-mm Spotlight tubular retractor system. Pathology confirmed the lesion to be a benign schwannoma. Postoperatively, the patient's symptoms resolved and she was discharged from the hospital on the second postoperative day. Postoperative MRI showed no residual tumor. The patient returned to normal activities after 2 weeks and remained asymptomatic with no neurological deficits at final 6 months follow-up.
Conclusion: Giant lumbar extradural schwannomas can be safely and completely resected using minimally invasive surgery without the need for facectomy or subsequent spinal fusion.
Keywords: Giant schwannoma; minimally invasive surgery; spinal neoplasm.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Minimally invasive resection of an extradural far lateral lumbar schwannoma with zygapophyseal joint sparing: surgical nuances and literature review.Case Rep Med. 2014;2014:739862. doi: 10.1155/2014/739862. Epub 2014 Sep 18. Case Rep Med. 2014. PMID: 25328530 Free PMC article.
-
Giant Lumbar Dumbbell Extradural Schwannoma in a Child.Asian J Neurosurg. 2019 Apr-Jun;14(2):535-537. doi: 10.4103/ajns.AJNS_132_18. Asian J Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 31143276 Free PMC article.
-
Minimally invasive removal of thoracic and lumbar spinal tumors using a nonexpandable tubular retractor.J Neurosurg Spine. 2013 Dec;19(6):708-15. doi: 10.3171/2013.9.SPINE121061. Epub 2013 Oct 18. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013. PMID: 24138063 Review.
-
Giant Dumbbell-Shaped Thoracic Schwannoma in an Elderly Patient Resected Through a Single-Stage Combined Laminectomy and Video-Assisted Thoracoscopy: Surgical Strategy and Technical Nuances.World Neurosurg. 2018 Nov;119:155-162. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.07.238. Epub 2018 Aug 6. World Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 30092472
-
Minimally invasive resection of extradural dumbbell tumors of thoracic spine: surgical techniques and literature review.Eur Spine J. 2016 Dec;25(12):4108-4115. doi: 10.1007/s00586-016-4677-z. Epub 2016 Jul 1. Eur Spine J. 2016. PMID: 27371333 Review.
Cited by
-
Minimally invasive resection of an extradural far lateral lumbar schwannoma with zygapophyseal joint sparing: surgical nuances and literature review.Case Rep Med. 2014;2014:739862. doi: 10.1155/2014/739862. Epub 2014 Sep 18. Case Rep Med. 2014. PMID: 25328530 Free PMC article.
-
Surgical management of Giant Lumbar Extradural Schwannoma: Report of 3 cases.Int J Spine Surg. 2015 May 26;9:18. doi: 10.14444/2018. eCollection 2015. Int J Spine Surg. 2015. PMID: 26114087 Free PMC article.
-
Minimally invasive tubular removal of spinal schwannoma and neurofibroma - a case series of 49 patients and review of the literature.Neurosurg Rev. 2024 Aug 10;47(1):418. doi: 10.1007/s10143-024-02656-x. Neurosurg Rev. 2024. PMID: 39123090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Giant Lumbar Dumbbell Extradural Schwannoma in a Child.Asian J Neurosurg. 2019 Apr-Jun;14(2):535-537. doi: 10.4103/ajns.AJNS_132_18. Asian J Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 31143276 Free PMC article.
-
Unusual cause of non-discogenic sciatica: Foraminal lumbar root schwannoma.Surg Neurol Int. 2014 Jul 30;5(Suppl 4):S208-10. doi: 10.4103/2152-7806.137755. eCollection 2014. Surg Neurol Int. 2014. PMID: 25184102 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander E, Wilkins RH, Rengachary SS, editors. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1985. Postlaminectomy kyphosis In: Neurosurgery; pp. 2293–7.
-
- Arts MP, Brand R, van den Akker ME, Koes BW, Bartels RH, Tan W, et al. Tubular Diskectomy vs Conventional Microdiskectomy for the Treatment of Lumbar Disk Herniation: 2-Year Results of a Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. Neurosurgery. 2011;69:135–44. - PubMed
-
- Bresnahan L, Ogden AT, Natarajan RN, Fessler RG. A biomechanical evaluation of graded posterior element removal for treatment of lumbar stenosis: Comparison of a minimally invasive approach with two standard laminectomy techniques. Spine. 2009;34:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Caputy AJ, Spence CA, Bejjani GK, Luessenhop AJ. The role of spinal fusion in surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis: A review. Neurosurg Focus. 1997;3:e3. - PubMed
-
- Celli P, Trillò G, Ferrante L. Spinal extradural schwannoma. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005;2:447–56. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

