Analysis of 16S rRNA environmental sequences using MEGAN
- PMID: 22369513
- PMCID: PMC3333176
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-S3-S17
Analysis of 16S rRNA environmental sequences using MEGAN
Abstract
Background: Metagenomics is a rapidly growing field of research aimed at studying assemblages of uncultured organisms using various sequencing technologies, with the hope of understanding the true diversity of microbes, their functions, cooperation and evolution. There are two main approaches to metagenomics: amplicon sequencing, which involves PCR-targeted sequencing of a specific locus, often 16S rRNA, and random shotgun sequencing. Several tools or packages have been developed for analyzing communities using 16S rRNA sequences. Similarly, a number of tools exist for analyzing randomly sequenced DNA reads.
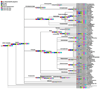
Results: We describe an extension of the metagenome analysis tool MEGAN, which allows one to analyze 16S sequences. For the analysis all 16S sequences are blasted against the SILVA database. The result output is imported into MEGAN, using a synonym file that maps the SILVA accession numbers onto the NCBI taxonomy.
Conclusions: Environmental samples are often studied using both targeted 16S rRNA sequencing and random shotgun sequencing. Hence tools are needed that allow one to analyze both types of data together, and one such tool is MEGAN. The ideas presented in this paper are implemented in MEGAN 4, which is available from: http://www-ab.informatik.uni-tuebingen.de/software/megan.
Figures

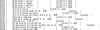


Similar articles
-
Microbial community analysis using MEGAN.Methods Enzymol. 2013;531:465-85. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407863-5.00021-6. Methods Enzymol. 2013. PMID: 24060133
-
Integrative analysis of environmental sequences using MEGAN4.Genome Res. 2011 Sep;21(9):1552-60. doi: 10.1101/gr.120618.111. Epub 2011 Jun 20. Genome Res. 2011. PMID: 21690186 Free PMC article.
-
VITCOMIC2: visualization tool for the phylogenetic composition of microbial communities based on 16S rRNA gene amplicons and metagenomic shotgun sequencing.BMC Syst Biol. 2018 Mar 19;12(Suppl 2):30. doi: 10.1186/s12918-018-0545-2. BMC Syst Biol. 2018. PMID: 29560821 Free PMC article.
-
Reference databases for taxonomic assignment in metagenomics.Brief Bioinform. 2012 Nov;13(6):682-95. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbs036. Epub 2012 Jul 10. Brief Bioinform. 2012. PMID: 22786784 Review.
-
High throughput sequencing methods for microbiome profiling: application to food animal systems.Anim Health Res Rev. 2012 Jun;13(1):40-53. doi: 10.1017/S1466252312000126. Anim Health Res Rev. 2012. PMID: 22853944 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and functional insights from the metagenome of an acidic hot spring microbial planktonic community in the Colombian Andes.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52069. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052069. Epub 2012 Dec 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23251687 Free PMC article.
-
ARK: Aggregation of Reads by K-Means for Estimation of Bacterial Community Composition.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 23;10(10):e0140644. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140644. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26496191 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Microbial Richness in Pelagic Sediment of Andaman Sea by Bacterial Tag Encoded FLX Titanium Amplicon Pyrosequencing (bTEFAP).Indian J Microbiol. 2012 Dec;52(4):544-50. doi: 10.1007/s12088-012-0310-y. Epub 2012 Sep 28. Indian J Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 24293708 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression of lactobacilli in murine forestomach biofilms.Microb Biotechnol. 2014 Jul;7(4):347-59. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12126. Epub 2014 Apr 4. Microb Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24702817 Free PMC article.
-
Application of ITS2 metabarcoding to determine the provenance of pollen collected by honey bees in an agroecosystem.Appl Plant Sci. 2015 Jan 5;3(1):apps.1400066. doi: 10.3732/apps.1400066. eCollection 2015 Jan. Appl Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 25606352 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pace N, Stahl D, Olsen G, Lane D. Analyzing natural microbial populations by rRNA sequences. American Society for Microbiology News. 1985;51:4–12.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

