Changes in cardiac biomarkers during doxorubicin treatment of pediatric patients with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia: associations with long-term echocardiographic outcomes
- PMID: 22370326
- PMCID: PMC3341148
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2010.30.3404
Changes in cardiac biomarkers during doxorubicin treatment of pediatric patients with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia: associations with long-term echocardiographic outcomes
Abstract
Purpose: Doxorubicin causes cardiac injury and cardiomyopathy in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Measuring biomarkers during therapy might help individualize treatment by immediately identifying cardiac injury and cardiomyopathy.
Patients and methods: Children with high-risk ALL were randomly assigned to receive doxorubicin alone (n = 100; 75 analyzed) or doxorubicin with dexrazoxane (n = 105; 81 analyzed). Echocardiograms and serial serum measurements of cardiac troponin T (cTnT; cardiac injury biomarker), N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP; cardiomyopathy biomarker), and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP; inflammatory biomarker) were obtained before, during, and after treatment.
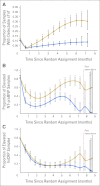
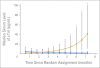
Results: cTnT levels were increased in 12% of children in the doxorubicin group and in 13% of the doxorubicin-dexrazoxane group before treatment but in 47% and 13%, respectively, after treatment (P = .005). NT-proBNP levels were increased in 89% of children in the doxorubicin group and in 92% of children in the doxorubicin-dexrazoxane group before treatment but in only 48% and 20%, respectively, after treatment (P = .07). The percentage of children with increased hsCRP levels did not differ between groups at any time. In the first 90 days of treatment, detectable increases in cTnT were associated with abnormally reduced left ventricular (LV) mass and LV end-diastolic posterior wall thickness 4 years later (P < .01); increases in NT-proBNP were related to an abnormal LV thickness-to-dimension ratio, suggesting LV remodeling, 4 years later (P = .01). Increases in hsCRP were not associated with any echocardiographic variables.
Conclusion: cTnT and NT-proBNP may hold promise as biomarkers of cardiotoxicity in children with high-risk ALL. Definitive validation studies are required to fully establish their range of clinical utility.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Lipshultz SE, Lipsitz SR, Mone SM, et al. Female sex and drug dose as risk factors for late cardiotoxic effects of doxorubicin therapy for childhood cancer. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1738–1743. - PubMed
-
- Krischer JP, Cuthbertson DD, Epstein S, et al. Risk factors for early anthracycline clinical cardiotoxicity in children: The pediatric oncology group experience. Prog Pediatr Cardiol. 1997;8:83–90.
-
- Nysom K, Holm K, Lipsitz SR, et al. Relationship between cumulative anthracycline dose and late cardiotoxicity in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:545–550. - PubMed
-
- Barry E, Alvarez JA, Scully RE, et al. Anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicty: Course, pathophysiology, prevention and management. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2007;8:1039–1058. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 HD052104/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HL078522/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL095127/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087000/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL094100/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 HL094100/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HD052102/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HL053392/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL087000/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA127642/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL079233/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL007188/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095127/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K30 HL004537/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007188/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HD80002/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HL087708/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA068484/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL078522/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI50274/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD052102/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R13 HL087708/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI050274/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HD052104/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- CA127642/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA068484/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL072705/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL053392/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL004537/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL072705/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

