Massively parallel functional dissection of mammalian enhancers in vivo
- PMID: 22371081
- PMCID: PMC3402344
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.2136
Massively parallel functional dissection of mammalian enhancers in vivo
Abstract
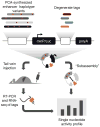
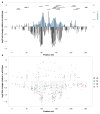
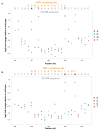
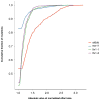
The functional consequences of genetic variation in mammalian regulatory elements are poorly understood. We report the in vivo dissection of three mammalian enhancers at single-nucleotide resolution through a massively parallel reporter assay. For each enhancer, we synthesized a library of >100,000 mutant haplotypes with 2-3% divergence from the wild-type sequence. Each haplotype was linked to a unique sequence tag embedded within a transcriptional cassette. We introduced each enhancer library into mouse liver and measured the relative activities of individual haplotypes en masse by sequencing the transcribed tags. Linear regression analysis yielded highly reproducible estimates of the effect of every possible single-nucleotide change on enhancer activity. The functional consequence of most mutations was modest, with ∼22% affecting activity by >1.2-fold and ∼3% by >2-fold. Several, but not all, positions with higher effects showed evidence for purifying selection, or co-localized with known liver-associated transcription factor binding sites, demonstrating the value of empirical high-resolution functional analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
In-depth functional dissection of enhancers.Nat Methods. 2012 Apr;9(4):322-3. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1963. Nat Methods. 2012. PMID: 22563600 No abstract available.
-
Dissecting genomic regulatory elements in vivo.Nat Biotechnol. 2012 Jun 7;30(6):504-6. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2266. Nat Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22678387 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cooper GM, Shendure J. Needles in stacks of needles: finding disease-causal variants in a wealth of genomic data. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12:628–640. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

