Propranolol reduces implicit negative racial bias
- PMID: 22371301
- PMCID: PMC3395337
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-012-2657-5
Propranolol reduces implicit negative racial bias
Abstract
Background: Implicit negative attitudes towards other races are important in certain kinds of prejudicial social behaviour. Emotional mechanisms are thought to be involved in mediating implicit "outgroup" bias but there is little evidence concerning the underlying neurobiology. The aim of the present study was to examine the role of noradrenergic mechanisms in the generation of implicit racial attitudes.
Methods: Healthy volunteers (n = 36) of white ethnic origin, received a single oral dose of the β-adrenoceptor antagonist, propranolol (40 mg), in a randomised, double-blind, parallel group, placebo-controlled, design. Participants completed an explicit measure of prejudice and the racial implicit association test (IAT), 1-2 h after propranolol administration.
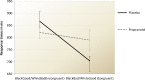
Results: Relative to placebo, propranolol significantly lowered heart rate and abolished implicit racial bias, without affecting the measure of explicit racial prejudice. Propranolol did not affect subjective mood.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that β-adrenoceptors play a role in the expression of implicit racial attitudes suggesting that noradrenaline-related emotional mechanisms may mediate negative racial bias. Our findings may also have practical importance given that propranolol is a widely used drug. However, further studies will be needed to examine whether a similar effect can be demonstrated in the course of clinical treatment.
Figures
Comment in
-
Measurement validity of tests for implicit negative bias.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012 Aug;222(4):721-2; author reply 723-4. doi: 10.1007/s00213-012-2765-2. Epub 2012 Jul 4. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2012. PMID: 22760482 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Guidance for Behavior Analysts in Addressing Racial Implicit Bias.Behav Anal Pract. 2021 Aug 11;15(4):1170-1183. doi: 10.1007/s40617-021-00631-2. eCollection 2022 Dec. Behav Anal Pract. 2021. PMID: 36605160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-Adrenoceptor blockade modulates fusiform gyrus activity to black versus white faces.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Aug;232(16):2951-8. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-3929-7. Epub 2015 Apr 22. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 25899791 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Racial discrimination by low-prejudiced whites. Facial movements as implicit measures of attitudes related to behavior.Psychol Sci. 2004 Nov;15(11):711-4. doi: 10.1111/j.0956-7976.2004.00746.x. Psychol Sci. 2004. PMID: 15482441
-
Implicit and explicit racial prejudice and stereotyping toward Black (vs. White) Americans: The prevalence and variation among genetic counselors in North America.J Genet Couns. 2023 Apr;32(2):397-410. doi: 10.1002/jgc4.1648. Epub 2022 Nov 7. J Genet Couns. 2023. PMID: 36341692 Free PMC article.
-
A review of neuroimaging studies of race-related prejudice: does amygdala response reflect threat?Front Hum Neurosci. 2014 Mar 27;8:179. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.00179. eCollection 2014. Front Hum Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24734016 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
What Bias Management Can Learn From Change Management? Utilizing Change Framework to Review and Explore Bias Strategies.Front Psychol. 2021 Dec 15;12:644145. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.644145. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34975601 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Sleep Restriction Increases Negative Implicit Attitudes Toward Arab Muslims.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 27;7(1):4285. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04585-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28655901 Free PMC article.
-
Noradrenaline effects on social behaviour, intergroup relations, and moral decisions.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016 Jul;66:54-60. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.03.031. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016. PMID: 27126289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Guidance for Behavior Analysts in Addressing Racial Implicit Bias.Behav Anal Pract. 2021 Aug 11;15(4):1170-1183. doi: 10.1007/s40617-021-00631-2. eCollection 2022 Dec. Behav Anal Pract. 2021. PMID: 36605160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interventions designed to reduce implicit prejudices and implicit stereotypes in real world contexts: a systematic review.BMC Psychol. 2019 May 16;7(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s40359-019-0299-7. BMC Psychol. 2019. PMID: 31097028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Converse JM, Presser S (1986) Survey questions, handcrafting the standardized questionnaire, series: quantitative applications in the social science 63. Thousand Oaks, California: SAGE Publications
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources