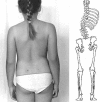
Functional scoliosis caused by leg length discrepancy
- PMID: 22371777
- PMCID: PMC3282518
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2010.14262
Functional scoliosis caused by leg length discrepancy
Abstract
Introduction: Leg length discrepancy (LLD) causes pelvic obliquity in the frontal plane and lumbar scoliosis with convexity towards the shorter extremity. Leg length discrepancy is observed in 3-15% of the population. Unequalized lower limb length discrepancy leads to posture deformation, gait asymmetry, low back pain and discopathy.
Material and methods: In the years 1998-2006, 369 children, aged 5 to 17 years (209 girls, 160 boys) with LLD-related functional scoliosis were treated. An external or internal shoe lift was applied.
Results: Among 369 children the discrepancy of 0.5 cm was observed in 27, 1 cm in 329, 1.5 cm in 9 and 2 cm in 4 children. During the first follow-up examination, within 2 weeks, the adjustment of the spine to new static conditions was noted and correction of the curve in 316 examined children (83.7%). In 53 children (14.7%) the correction was observed later and was accompanied by slight low back pain. The time needed for real equalization of limbs was 3 to 24 months. The time needed for real equalization of the discrepancy was 11.3 months.
Conclusions: Leg length discrepancy equalization results in elimination of scoliosis. Leg length discrepancy < 2 cm is a static disorder; that is why measurements should be performed in a standing position using blocks of adequate thickness and the position of the posterior superior iliac spine should be estimated.
Keywords: functional scoliosis; leg length discrepancy; low back pain.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Leg Length Discrepancy and Nonspecific Low Back Pain: 3-D Stereophotogrammetric Quantitative Posture Evaluation Confirms Positive Effects of Customized Heel-Lift Orthotics.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Feb 10;9:743132. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.743132. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35223808 Free PMC article.
-
A case report of severe degenerative lumbar scoliosis associated with windswept lower limb deformity.BMC Surg. 2020 Sep 3;20(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s12893-020-00857-x. BMC Surg. 2020. PMID: 32883265 Free PMC article.
-
Scoliosis Caused by Limb-Length Discrepancy in Children.Asian Spine J. 2020 Dec;14(6):801-807. doi: 10.31616/asj.2019.0374. Epub 2020 May 21. Asian Spine J. 2020. PMID: 32429019 Free PMC article.
-
Leg length discrepancy.Gait Posture. 2002 Apr;15(2):195-206. doi: 10.1016/s0966-6362(01)00148-5. Gait Posture. 2002. PMID: 11869914 Review.
-
Shoe Lifts for Leg Length Discrepancy in Adults With Common Painful Musculoskeletal Conditions: A Systematic Review of the Literature.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2018 May;99(5):981-993.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2017.10.027. Epub 2017 Dec 9. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2018. PMID: 29229292
Cited by
-
Postoperative improvement in leg length discrepancy in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis differs between right and left legs.N Am Spine Soc J. 2022 Mar 21;10:100114. doi: 10.1016/j.xnsj.2022.100114. eCollection 2022 Jun. N Am Spine Soc J. 2022. PMID: 35464492 Free PMC article.
-
Etiological Theories of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Past and Present.Open Orthop J. 2017 Dec 29;11:1466-1489. doi: 10.2174/1874325001711011466. eCollection 2017. Open Orthop J. 2017. PMID: 29399224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leg Length Discrepancy and Nonspecific Low Back Pain: 3-D Stereophotogrammetric Quantitative Posture Evaluation Confirms Positive Effects of Customized Heel-Lift Orthotics.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Feb 10;9:743132. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.743132. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35223808 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of therapeutic footwear for children: A systematic review.J Foot Ankle Res. 2020 May 13;13(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13047-020-00390-3. J Foot Ankle Res. 2020. PMID: 32404124 Free PMC article.
-
Limb salvage reconstruction of the lower limb with complex ankle arthrodesis and magnetic internal lengthening nail.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2024 May;34(4):1877-1882. doi: 10.1007/s00590-024-03863-4. Epub 2024 Mar 5. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2024. PMID: 38441634
References
-
- Aaron AD, Eilert ED. Results of Wagener and Ilizarov methods of limb-lengtening. J Bone Joint Surg A. 1996;78:20–9. - PubMed
-
- D'Amico M. Scoliosis and leg asymmetries: a reliable approach to assess wedge solutions efficacy. Studies in health technology and informatics. 2002;88:285–9. - PubMed
-
- Łabaziewicz L, Nowakowski A. Scoliosis and faulty posture [Polish] Chir Narz Ruchu Ortop Pol. 1996;61:247–50. - PubMed
-
- Rose R, et al. Pediatric leg length discrepancy: causes and treatments. Orthop Nurs. 1999;18:21–30. - PubMed
-
- Skwarcz A, Majcher P. Medical rehabilitation [Polish] Wroclaw: Urban & Partner; 2003. Rehabilitation in scoliosis; pp. 185–237.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources